Microsoft Solution for Supplier
Enablement
Deployment Guide
Microsoft Corporation
Service Release 1, May 2002
Applies to:
Microsoft Solution for Supplier
Enablement
Microsoft Commerce Server 2002
Microsoft
BizTalk Server 2002
Summary Deploy the Microsoft Solution for Supplier
Enablement (MSSE). Installation procedures for deploying the MSSE in a
medium organization deployment environment are provided. (95 printed
pages)
Contents
Introduction
Installation Scope
Deployment Reference Model
Medium Organization Deployment Details
Installing Solution Components
Locking Down the System
Verifying Installation
Known Issues
URL Resources
Introduction
The Microsoft® Solution for Supplier Enablement (MSSE) integrates a
number of Microsoft products into a solution that allows suppliers of
various sizes to begin trading electronically with their trading partners.
These products include Microsoft BizTalk® Server 2002, Microsoft Commerce
Server 2002, Microsoft SQL Server™ 2000, and Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator
for Suppliers Service Release 1 (AFS).
This guide provides specific installation procedures for deploying the
MSSE in a medium organization deployment environment to support catalog
publishing and order reception functionality.
Reader Guidance
Before deploying AFS, the entire deployment team should review the
"Known Issues" section at the end of this document. Upon successful
deployment, operations personnel should become familiar with the product
documentation for BizTalk Server, Commerce Server, SQL Server, and BizTalk
Accelerator for Suppliers Service Release 1 (AFS).
Installation Scope
While there are many different ways in which to deploy AFS, this
document focuses primarily on deploying AFS in a medium organization
deployment environment. Using this deployment example as a model, you can
modify the appropriate portions of the deployment to suit your particular
environment. In addition to the medium deployment, this document also
includes information for development and core-medium deployments in the
areas of hardware and software requirements, server and network
architecture, and functionality verification.
Concepts and Features
The following table describes the key concepts that are used in this
document.
| Concept |
Description |
| Deployment architecture |
Refers to the logical design of a
specific deployment. For example, a deployment might consist of a
perimeter network (also known as demilitarized zone or DMZ) and a
private intranet zone. |
| Network architecture |
Refers to the physical design of a
specific deployment. For example, the DMZ of a specific deployment
might consist of one domain controller and three Web servers. |
| Network Load Balancing |
Refers to the load-balancing feature in
Microsoft Windows® 2000 Advanced Server that distributes incoming
client requests across multiple Web servers. |
| Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA)
Server |
Refers to the servers that are used for
securing and caching data. |
| Domain Name System (DNS) servers |
Refers to the servers that are used in
resolving domain names to IP addresses. |
Planning Checklist
Before deploying the solution, you must determine which type of
deployment to implement. To identify a suitable deployment architecture,
consider the following factors:
- Expected orders/second
- Average number of line items in an order
- Average size of an order
- Frequency at which catalogs are published
- Catalog size
- Number of products in a catalog
- Number of variants in a catalog
- Expected remote shopping requests/second
The results of gathering this information should help you identify a
suitable deployment architecture. After the deployment architecture has
been determined, make sure you have the following elements:
- Required hardware for the deployment
- Required software and associated licenses
- High-speed Internet access and fully qualified domain names (FQDN)
for the solution site
- Security policy
- Hubs
Installing and Deploying the Solution
When deploying AFS, you have a number of options depending on the
amount of order traffic and sales that you expect. Microsoft developer
tools and Windows Server System servers have the advantage of being highly
scalable, allowing businesses to start off small and then scale to larger
enterprise-level designs with small, incremental investments. This section
describes the three most typical deployments: development, core-medium,
and medium.
Development Deployment
The development deployment involves a two-server architecture that
serves as a development and testing environment. This deployment
architecture has the simplest configuration, yet is robust enough for a
solution to be developed and tested on. The development deployment is not
supported in production environments.
The following figure shows the architecture of the development
deployment.
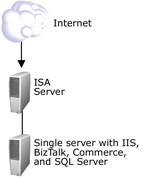
Figure 1
In this deployment architecture, all of the software, including all of
the components for AFS, are installed on a single server. The single
server is protected behind a firewall, which can be a hardware firewall or
Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server. On this
firewall, port 80 must be opened for HTTP and port 443 must be opened for
HTTPS. After the solution is developed and tested on the development
deployment architecture, it can be migrated to either the core-medium or
medium deployment architecture.
For detailed information about installing the MSSE in the development
deployment, see the "Installing AFS on One Computer" section of the AFS
Installation Guide. The AFS Installation Guide is on the product CD in the
file <drive>:\Program Files\Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for
Suppliers\Documentation\installation_guide.htm.
Core-Medium Deployment
The core-medium deployment, designed for small businesses, consists of
a three-server architecture. This deployment architecture is designed for
sites with low volume. For supporting production environments, this
architecture has the simplest and most economical configuration. The
core-medium deployment is a good starting point for businesses that have
developed and tested their solution on the development deployment, but are
not ready to scale to the medium deployment.
The following figure shows the architecture of the core-medium
deployment.

Figure 2
The Web server running BizTalk Server, Commerce Server, and AFS
receives all incoming client requests. The SQL Server handles all
transactions with the database. The two servers are protected by a
firewall, which can be a hardware firewall or an ISA Server. On the
firewall, port 80 must be opened for HTTP and port 443 must be opened for
HTTPS.
As the volume of traffic and business increases, this deployment
architecture can scale to the medium deployment architecture, where an
additional Web server is used to handle client requests, and XML
transformation is isolated onto a separate BizTalk Server.
For detailed information about installing the MSSE in the core-medium
deployment, see the "Installing AFS on Multiple Computers" section of the
AFS Installation Guide. The AFS Installation Guide is on the product CD in
the file <drive>:\Program Files\Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator
for Suppliers\Documentation\installation_guide.htm.
Medium Deployment
The medium deployment consists of a nine-server architecture. This
deployment architecture is designed for medium-sized organizations that
expect sustained activity on the site and want flexibility for scaling.
This architecture has the most practical configuration because the design
addresses load balancing and security concerns.
The following figure shows the architecture of the medium
deployment.

Figure 3
Client requests are received by the Web server in the perimeter network
(also known as demilitarized zone or DMZ). This server provides content
for the supplier site, while requests containing sensitive data (requests
for confirm.asp, crdtcard.asp, and _recvpo.asp) are processed by the
Commerce Server Business Desk server running in the intranet. Because the
processing of these types of requests consumes more resources, the
Business Desk server running in the intranet reduces the load on the DMZ
Web server and allows the Web server to serve content exclusively.
To prevent the security of the intranet from being compromised, the
intranet firewall only allows access to the intranet through port 1433 for
SQL Server, port 1801 for Message Queuing, and port 8080 for HTTP.
Requests received on other ports are discarded.
For detailed information about installing the MSSE in the medium
deployment, see the "Installing AFS on Multiple Computers" section of the
AFS Installation Guide. The AFS Installation Guide is on the product CD in
the file <drive>:\Program Files\Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator
for Suppliers\Documentation\installation_guide.htm.
Deployment Reference
Model
This section provides general information about the minimum hardware
requirements, recommended hardware configuration, and solution components
for your deployment.
Before implementing the solution, you should identify the hardware
requirements for your particular deployment architecture. All hardware
used in the deployment should comply with the Microsoft Hardware Compatibility List
(HCL).
Minimum Hardware Requirements
Each server in the deployment should meet the following minimum
hardware requirements:
- 400 MHz or faster Pentium-compatible CPU
- 256 MB of RAM (128 MB of RAM is adequate for a development
environment)
- 6.0 GB of hard disk space
- CD-ROM drive
- Network adapter card
- VGA or Super VGA monitor
- Microsoft Mouse or compatible pointing device
In your production environment, the volume of traffic on your Web site
might dictate more stringent hardware requirements for Web servers.
Recommended Hardware Configuration
The following table lists the recommended hardware configuration for
the development deployment.
| Server |
Processor |
RAM |
Hard disk size |
Network adapters |
| Single |
Single 500 MHz |
512 MB |
8 GB |
1 |
| ISA Server |
Single 500 MHz |
512 MB |
8 GB |
2 |
The following table lists the recommended hardware configuration for
the core-medium deployment.
| Server |
Processor |
RAM |
Hard disk size |
Network adapters |
| Web server |
Dual 700 MHz |
1 GB |
12 GB |
1 |
| SQL Server |
Quad 500 MHz |
1 GB |
25 GB |
1 |
| ISA Server |
Single 500 MHz |
512 MB |
8 GB |
2 |
The following table lists the recommended hardware configuration for
the medium deployment.
| Server |
Processor |
RAM |
Hard disk size |
Network adapters |
| 3 X DMZ Web server |
Dual 700 MHz |
1 GB |
12 GB |
2 |
| External ISA Server |
Single 500 MHz |
512 MB |
8 GB |
3 |
| Business Desk server |
Dual 700 MHz |
1 GB |
12 GB |
1 |
| BizTalk Server |
Dual 700 MHz |
1 GB |
12 GB |
1 |
| Intranet ISA Server |
Single 500 MHz |
512 MB |
8 GB |
3 |
| SQL Server |
Quad 500 MHz |
1 GB |
25 GB |
1 |
| DC/DNS Servers |
Single 500 MHz |
512 MB |
8 GB |
1 |
Solution Components
This section lists the required software products that each server uses
for each deployment architecture.
Development Deployment
For the development deployment, the single server uses the following
software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Internet Information Services (IIS) 5.0
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q294831)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q317177)
Note In Internet
Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321827 and follow the online installation
instructions.
- Message Queuing (also known as MSMQ)
- Internet Explorer 5.5 Service Pack 2
- Microsoft XML Parser (MSXML) version 3.0 with Service Pack 2
- SQL Server 2000 Standard Edition with Service Pack 2
- OLAP 2000 Standard Edition with Service Pack 2
- BizTalk Server 2002 Standard Edition
- Commerce Server 2002 Standard Edition
- .NET Framework
- Microsoft Visual Basic® 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5
- Microsoft Visio® 2002 with Service Release 1
- BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Service Release 1
- Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC) 2.7
- MDAC 2.7 Rollup
- OWC 10
- MSXML 4.0
- IIS Lockdown Tool 2.1
The firewall server uses the following software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- ISA Server 2000 Standard Edition with Service Pack 1
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix Q315764
Note In Internet
Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321828 and follow the online installation
instructions.
Core-Medium Deployment
For the core-medium deployment, the Web server uses the following
software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Internet Information Services (IIS) 5.0
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q294831)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q317177)
Note In Internet
Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321827 and follow the online installation
instructions.
- Message Queuing
- MSXML version 3.0 with Service Pack 2
- BizTalk Server 2002 Standard Edition
- Commerce Server 2002 Standard Edition
- .NET Framework
- Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5
- BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Service Release 1
- MDAC 2.7
- MDAC 2.7 Rollup
- IIS Lockdown Tool 2.1
The database server uses the following software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- SQL Server 2000 Standard Edition with Service Pack 2
- OLAP 2000 Standard Edition with Service Pack 2
The firewall server uses the following software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- ISA Server 2000 Standard Edition with Service Pack 1
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix Q315764
Note In Internet
Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321828 and follow the online installation
instructions.
Medium Deployment
For the medium deployment, the Web server uses the following software
products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Internet Information Services (IIS) 5.0
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q294831)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q317177)
Note In Internet
Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321827 and follow the online installation
instructions.
- Message Queuing
- MSXML version 3.0 with Service Pack 2
- Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
- .NET Framework
- Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5
- BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Service Release 1
- MDAC 2.7
- MDAC 2.7 Rollup
- IIS Lockdown Tool 2.1
The database server uses the following software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition with Service Pack 2
- OLAP 2000 Enterprise Edition with Service Pack 2
The Business Desk server uses the following software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Internet Information Services (IIS) 5.0
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q294831)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q317177)
Note In Internet
Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321827 and follow the online installation
instructions.
- Message Queuing
- MSXML version 3.0 with Service Pack 2
- Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
- .NET Framework
- Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5
- BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Service Release 1
- MDAC 2.7
- MDAC 2.7 Rollup
- MSXML 4.0
- IIS Lockdown Tool 2.1
The BizTalk Server uses the following software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Internet Information Services (IIS) 5.0
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q294831)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q317177)
Note In Internet
Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321827 and follow the online installation
instructions.
- Message Queuing
- MSXML version 3.0 with Service Pack 2
- BizTalk Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
- BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Service Release 1
- IIS Lockdown Tool 2.1
The firewall servers use the following software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- ISA Server Standard Edition 2000 with Service Pack 1
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix Q315764
Note In Internet
Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321828 and follow the online installation
instructions.
The DC/DNS server uses the following software products:
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
On the external firewall server, ports 80 and 443 should be opened for
HTTP and HTTPS, respectively. On the internal firewall server, inbound
ports 1433 and 1801 should be opened for SQL Server and Message Queuing,
respectively. The internal firewall server should also have outbound port
8080 opened for HTTP.
Medium Organization
Deployment Details
This section provides detailed instructions for the medium organization
deployment. This deployment involves the following primary stages:
- Configure the base platform.
- Establish communication.
- Set up the intranet domain.
- Cluster the Web servers.
- Install solution components.
In the first stage, you install the base platform (including the
operating system) on each server. When establishing communication in the
second stage, you configure all IP addresses on all network adapters. In
the third stage, you configure the domain controller. In the fourth stage,
you configure Network Load Balancing on the DMZ Web cluster. In the fifth
stage, you install and configure all of the proper software on each
server.
Note Before starting the
deployment, you should be familiar with the issues listed in the "Known
Issues" section at the end of this document.
The following figure shows an example of the network topology and IP
address configuration for the medium deployment. This figure and the
subsequent table can serve as useful references when performing the
deployment.

Figure 4
Deployment Worksheet
The following table lists the IP addresses assigned to the various
network adapters on each server.
| Server |
Network adapter |
IP address |
Virtual IP (VIP) |
Default gateway |
DNS entry |
| External ISA Server |
1 (public) |
Public, static IP |
|
Internet gateway |
Public DNS |
| |
2 (private) |
10.10.0.100 |
|
|
|
| |
3 (dedicated) |
10.50.0.101 |
|
|
|
| DMZ Web server 1 |
1 (public) |
10.10.0.1 |
10.10.0.10 |
10.10.0.100 |
|
| |
2 (private) |
10.20.0.1 |
|
|
|
| DMZ Web server 2 |
1 (public) |
10.10.0.2 |
10.10.0.10 |
10.10.0.100 |
|
| |
2 (private) |
10.20.0.2 |
|
|
|
| DMZ Web server 3 |
1 (public) |
10.10.0.3 |
10.10.0.10 |
10.10.0.100 |
|
| |
2 (private) |
10.20.0.3 |
|
|
|
| Intranet ISA Server |
1 (public) |
10.20.0.100 |
|
|
|
| |
2 (private) |
10.30.0.100 |
|
|
10.30.0.200 |
| |
3 (dedicated) |
10.50.0.100 |
|
10.50.0.101 |
|
| Intranet DC/DNS server |
1 |
10.30.0.200 |
|
10.30.0.100 |
10.30.0.200 |
| BizTalk Server |
1 |
10.30.0.1 |
|
10.30.0.100 |
10.30.0.200 |
| Business Desk Server |
1 |
10.30.10.1 |
|
10.30.0.100 |
10.30.0.200 |
| SQL Server |
1 |
10.30.20.1 |
|
10.30.0.100 |
10.30.0.200 |
Configuring the Base Platform
Use the following procedure to configure the base platform.
To configure the base platform
- Install Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 2 on all
servers.
When installing Windows 2000 Advanced Server, do not install Message
Queuing. This feature will be installed later in the deployment process,
after other resources have been configured. To prevent Message Queuing
from being installed, clear the Message Queuing Services check
box in the Windows Components Wizard.
- When installing Windows 2000 Advanced Server, install Internet
Information Services (IIS) 5.0 on the BizTalk Server, the Business Desk
server, and the DMZ Web servers.
- The following hotfixes are required by the BizTalk Server, the
Business Desk server, and the DMZ Web servers:
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q294831)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Hotfix for IIS (Q317177)
Note In Internet
Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321827 and follow the online installation
instructions.
- The following hotfix is required by the ISA, SQL, and DC/DNS
Servers:
- Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 Security Rollup Package (Q311401)
After configuring the base platform, it might be useful to create a
backup image of each server. This backup image allows you to recover the
server without re-installing all of the solution components in the event
of failure.
Establishing Communication
Before installing and configuring the solution components on each
server, you need to establish communication by connecting the appropriate
network cables and configuring the IP addresses on all servers. Then, you
need to join each server to the appropriate domain. This section provides
detailed instructions for completing these tasks.
When establishing network connectivity on each server, see the network
figure and deployment worksheet in the "Medium Organization Deployment
Details" section.
Connecting the Intranet DC/DNS Server
The following figure shows the network configuration for the
intranet DC/DNS server.

Figure 5
Connecting and Renaming the Network Adapter
You should rename the network adapter from Local Area Connection
to an informative name, such as Intranet. Use the following
procedure to connect and rename the network adapter.
To connect and rename the network adapter
- Connect a network cable from the network adapter on the intranet
DC/DNS server to Hub 3.
- On the desktop of the intranet DC/DNS server, right-click My
Network Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection, and then click Rename.
- Type Intranet, and then press ENTER.
Configuring the Network Adapter on the Intranet DC/DNS
Server
Use the following procedure to configure the Intranet network adapter
on the intranet DC/DNS server.
To configure the Intranet network adapter on the intranet DC/DNS
server
- On the desktop of the intranet DC/DNS server, right-click My
Network Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Intranet, and then click Properties.
- In the Intranet Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.30.0.200 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
10.30.0.100 |
- Select Use the following DNS server addresses, and do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Preferred DNS Server |
10.30.0.200 |
- Click OK.
- In the Intranet Properties dialog box, click
OK.
Connecting the BizTalk Server
The following figure shows the network configuration for the
BizTalk Server.

Figure 6
Connecting and Renaming the Network Adapter
You should rename the network adapter from Local Area Connection to an
informative name, such as Intranet. Use the following procedure to connect
and rename the network adapter.
To connect and rename the network adapter
- Connect a network cable from the network adapter on the BizTalk
Server to Hub 3.
- On the desktop of the BizTalk Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection, and then click Rename.
- Type Intranet, and then press ENTER.
Configuring the Network Adapter on the BizTalk Server
Use the following procedure to configure the Intranet network adapter
on the BizTalk Server.
To configure the Intranet network adapter on the BizTalk Server
- On the desktop of the BizTalk Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Intranet, and then click Properties.
- In the Intranet Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.30.0.1 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
10.30.0.100 |
- Select Use the following DNS server addresses, and do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Preferred DNS Server |
10.30.0.200 |
- Click OK.
- In the Intranet Properties dialog box, click
OK.
Connecting the Business Desk Server
The following figure shows the network configuration for the
Business Desk server.

Figure 7
Connecting and Renaming the Network Adapter
You should rename the network adapter from Local Area Connection to an
informative name, such as Intranet. Use the following procedure to connect
and rename the network adapter.
To connect and rename the network adapter
- Connect a network cable from the network adapter of the Business
Desk server to Hub 3.
- On the desktop of the Business Desk server, right-click My
Network Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection, and then click Rename.
- Type Intranet, and then press ENTER.
Configuring the Network Adapter on the Business Desk Server
Use the following procedure to configure the Intranet network adapter
on the Business Desk server.
To configure the Intranet network adapter on the Business Desk
server
- On the desktop of the Business Desk server, right-click My
Network Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Intranet, and then click Properties.
- In the Intranet Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.30.10.1 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
10.30.0.100 |
- Select Use the following DNS server addresses, and do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Preferred DNS Server |
10.30.0.200 |
- Click OK.
- In the Intranet Properties dialog box, click OK.
Connecting the SQL Server
The following figure shows the network configuration for the SQL
Server.

Figure 8
Connecting and Renaming the Network Adapter
You should rename the network adapter from Local Area Connection to an
informative name, such as Intranet. Use the following procedure to connect
and rename the network adapter.
To connect and rename the network adapter
- Connect a network cable from the network adapter of the SQL Server
to Hub 3.
- On the desktop of the SQL Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection, and then click Rename.
- Type Intranet, and then press ENTER.
Configuring the Network Adapter on the SQL Server
Use the following procedure to configure the Intranet network adapter
on the SQL Server.
To configure the Intranet network adapter on the SQL Server
- On the desktop of the SQL Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Intranet, and then click Properties.
- In the Intranet Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.30.20.1 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
10.30.0.100 |
- Select Use the following DNS server addresses, and do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Preferred DNS Server |
10.30.0.200 |
- Click OK.
- In the Intranet Properties dialog box, click OK.
Connecting the Intranet ISA Server
For the medium deployment, the intranet ISA Server requires three
network adapters — one public adapter for communicating with the Web
servers in the perimeter network (also called demilitarized zone or DMZ),
one private adapter for communicating with the servers in the intranet,
and one dedicated adapter for communicating with the external ISA
Server.
The following figure shows the network configuration for the intranet
ISA Server.

Figure 9
Connecting and Renaming the Network Adapters
You should rename the network adapters from Local Area Connection,
Local Area Connection 2, and Local Area Connection 3 to more informative
names, such as Public, Private, and Dedicated. Use the following procedure
to connect and rename the network adapters.
To connect and rename the network adapters
- Connect a network cable from the first network adapter of the
intranet ISA Server to Hub 2 (the same hub connected to the private
network adapters of the DMZ Web cluster). Communication with the DMZ Web
cluster occurs over this network adapter.
- Connect a network cable from the second network adapter to Hub 3.
Communication with the intranet occurs over this network adapter.
- Connect a network cable from the third network adapter to Hub 4.
Communication with the external ISA Server occurs over this network
adapter.
- On the desktop of the intranet ISA Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection, and then click Rename. This network
adapter should correspond with the network adapter you connected to Hub
2 in step 1.
- Type Public, and then press ENTER.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection 2, and then click Rename. This
network adapter should correspond with the network adapter you connected
to Hub 3 in step 2.
- Type Private, and then press ENTER.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection 3, and then click Rename. This
network adapter should correspond with the network adapter you connected
to Hub 4 in step 3.
- Type Dedicated, and then press ENTER.
Configuring the Public Network Adapter
To communicate with the Web servers in the DMZ, you need to set the
TCP/IP properties of the Public network adapter.
To set the TCP/IP properties of the Public network adapter
- On the desktop of the intranet ISA Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Public, and then click Properties.
- In the Public Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.20.0.100 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
Leave blank. |
- Click Advanced.
- In the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box, on the DNS
tab, select Append these DNS suffixes (in order), and then click
Add.
- In the TCP/IP Domain Suffix dialog box, type
contoso.com, and then click Add.
- In the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box, click OK.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box,
click OK.
- In the Public Properties dialog box, click OK.
Configuring the Private Network Adapter
To communicate with other servers in the intranet, you need to set the
TCP/IP properties of the Private network adapter.
To set the TCP/IP properties of the Private network adapter
- On the desktop of the intranet ISA Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Private, and then click Properties.
- In the Private Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.30.0.100 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
Leave blank. |
- Select Use the following DNS server addresses, and do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Preferred DNS Server |
10.30.0.200 |
- Click OK.
- In the Private Properties dialog box, click OK.
Configuring the Dedicated Network Adapter
To communicate with the external ISA Server, you need to set the TCP/IP
properties of the Dedicated network adapter.
To set the TCP/IP properties of the Dedicated network adapter
- On the desktop of the intranet ISA Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Dedicated, and then click Properties.
- In the Dedicated Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.50.0.100 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
10.50.0.101 |
- Click OK.
- In the Dedicated Properties dialog box, click OK.
Connecting the DMZ Web Cluster
The DMZ Web cluster uses Windows 2000 Network Load Balancing to
distribute incoming client requests across the multiple members of the DMZ
Web cluster. Each server in the cluster requires two network adapters —
one load-balanced adapter for communicating with clients on the public
network, and one cluster adapter for communicating with the private
network (or intranet). For third-party load balancing devices, only one
network adapter might be required.
The following figure shows the network configuration of the DMZ Web
cluster.

Figure 10
Connecting and Renaming the Network Adapters
You should rename the network adapters from Local Area Connection and
Local Area Connection 2 to more informative names, such as Public and
Private. Use the following procedure on each Web server to connect and
rename the network adapters.
To connect and rename the network adapters
- Connect a network cable from the first network adapter of the Web
server to Hub 1.
- Connect a network cable from the second network adapter of the Web
server to Hub 2.
- On the desktop of the Web server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections dialog box,
right-click Local Area Connection, and then click Rename.
This network adapter should correspond with the network adapter you
connected to Hub 1 in step 1.
- Type Public, and then press ENTER.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection 2, and then click Rename. This
network adapter should correspond with the network adapter you connected
to Hub 2 in step 2.
- Type Private, and then press ENTER.
Configuring the Public Network Adapter
On Web server 1, set the TCP/IP properties of the Public network
adapter.
To set the TCP/IP properties of the Public network adapter
- On the desktop of the Web server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Public, and then click Properties.
- In the Public Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.10.0.1 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
10.10.0.100 |
- Click Advanced.
- In the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box, on the
WINS tab, select Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP, and then
click OK.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box,
click OK.
- In the Public Properties dialog box, clear the check box
beside Client for Microsoft Networks and File and Printer Sharing for
Microsoft Networks, and then click OK.
On Web servers 2 and 3, follow the same procedure using
10.10.0.2 and 10.10.0.3 as the IP addresses,
respectively.
Configuring the Private Network Adapter
On Web server 1, change the TCP/IP settings of the Private network
adapter.
To change the TCP/IP settings of the Private network
adapter
- On the desktop of the Web server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Private, and then click Properties.
- In the Private Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.20.0.1 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
Leave blank. |
- Click OK.
- In the Private Properties dialog box, click OK.
On Web servers 2 and 3, follow the same procedure using
10.20.0.2 and 10.20.0.3 as the IP addresses,
respectively.
Connecting the External ISA Server
For the medium deployment, the external ISA Server requires three
network adapters — one public adapter for communicating with the Internet,
one private adapter for communicating with the servers in the DMZ, and one
dedicated adapter for communicating with the intranet ISA Server.
The following figure shows the network configuration for the
external ISA Server.

Figure 11
Connecting and Renaming the Network Adapters
You should rename the network adapters from Local Area Connection,
Local Area Connection 2, and Local Area Connection 3 to more informative
names, such as Public, Private, and Dedicated. Use the following procedure
to connect and rename the network adapters.
To connect and rename the network adapters
- Connect a network cable from the first network adapter of the
external ISA Server to the direct tap. This direct tap should be a
direct connection to the Internet.
- Connect a network cable from the second network adapter of the
external ISA Server to Hub 1 (the same hub connected to the
Public network adapters of the DMZ Web cluster).
- Connect a network cable from the third network adapter of the
external ISA Server to Hub 4 (the same hub connected to the intranet ISA
Server).
- On the desktop of the external ISA Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection, and then click Rename. This network
adapter should correspond with the network adapter you connected to the
direct tap in step 1.
- Type Public, and then press ENTER.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection 2, and then click Rename. This
network adapter should correspond with the network adapter you connected
to Hub 1 in step 2.
- Type Private, and then press ENTER.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection 3, and then click Rename. This
network adapter should correspond with the network adapter you connected
to Hub 4 in step 3.
- Type Dedicated, and then press ENTER.
Configuring the Public Network Adapter
To communicate with the Internet, you need to set the TCP/IP properties
of the Public network adapter.
To set the TCP/IP properties of the Public network adapter
- On the desktop of the external ISA Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Public, and then click Properties.
- In the Public Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
type the public IP address in the IP address box. Type the
appropriate subnet mask and default gateway in the Subnet mask
and Default gateway boxes, respectively.
- Select Use the following DNS server addresses, and then type
the IP address for your DNS server in the Preferred DNS server
box and an alternative IP address in the Alternate DNS server box
(if applicable).
- Click Advanced.
- In the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box, on the
WINS tab, select Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP, and then
click OK.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box,
click OK.
- In the Public Properties dialog box, clear the check box for
Client for Microsoft Networks and File and Printer Sharing for
Microsoft Networks, and then click OK.
Configuring the Private Network Adapter
To communicate with the Web servers in the DMZ, you need to set the
TCP/IP properties of the Private network adapter.
To set the TCP/IP properties of the Private network adapter
- On the desktop of the external ISA Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Private, and then click Properties.
- In the Private Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.10.0.100 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
Leave blank. |
- Click OK.
- In the Private Properties dialog box, click OK.
Configuring the Dedicated Network Adapter
To communicate with the intranet ISA Server, you need to set the TCP/IP
properties of the Dedicated network adapter.
To set the TCP/IP properties of the Dedicated network adapter
- On the desktop of the external ISA Server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Dedicated, and then click Properties.
- In the Dedicated Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, on
the General tab, select Use the following IP address, and
do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.50.0.101 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
Leave blank. |
- Click OK.
- In the Dedicated Properties dialog box, click OK.
Setting Up the Intranet Domain
This section describes how to configure your DC/DNS server; create the
Contoso domain, new hosts, and the necessary domain accounts; and how to
join the intranet servers to the Contoso domain.
Configuring the Intranet DC/DNS Server
Use the following procedure to configure the intranet DC/DNS
server.
To launch the Active Directory Installation Wizard and configure
your Windows 2000 Advanced Server as an intranet DC/DNS server
- Click Start, and then click Run.
- In the Run dialog box, in the Run box, type
dcpromo, and then click OK.
- In the Welcome to the Active Directory Installation Wizard
screen, click Next.
- In the Domain Controller Type screen, select Domain
controller for a new domain, and then click Next.
- In the Create Tree or Child Domain screen, select Create a
new domain tree, and then click Next.
- In the Create or Join Forest screen, select Create a new
forest of domain trees, and then click Next.
- In the New Domain Name screen, type the full DNS name for the
new domain, and then click Next. For example, the full DNS name
for your domain might be Contoso.com.
- In the NetBIOS Domain Name screen, click Next to use
the default NetBIOS Domain name of CONTOSO.
- In the Database and Log Locations screen, click Next
to store the Active Directory® database and log in the default location.
To specify different locations, click Browse and select the
appropriate directory.
- In the Shared System Volume screen, click Next to use
the default location for the Sysvol folder.
- In the Active Directory Installation Wizard dialog box, click
OK.
- In the Configure DNS screen, select Yes, install and
configure DNS on this computer (recommended), and then click
Next.
- In the Permissions screen, select Permissions compatible
only with Windows 2000 servers, and then click Next.
- In the Directory Services Restore Mode Administrator Password
screen, type and confirm a password, and then click Next.
- In the Summary screen, review the information to ensure that
it is accurate, and then click Next.
The installation process starts. Note that you may be required to
insert the Windows 2000 CD into the CD-ROM drive. Do not skip the DNS
installation step of this process; allow the wizard to install DNS.
- In the Completing the Active Directory Installation Wizard
screen, click Finish.
- Restart the server.
Creating New Hosts on the Intranet DC/DNS Server
You must add four new hosts — one for each of the three DMZ Web
servers, and one Business Desk server in the intranet.
To add a host for the first DMZ Web server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then select DNS.
- In the DNS window, expand <servername>,
expand Forward Lookup Zone, right-click contoso.com, and
then click New Host.
- In the New Host dialog box, in the Name box, type the
name of Web server 1. In the IP address box, type
10.20.0.1, and then click Add Host.
- In the DNS dialog box informing you that the host record was
successfully created, click OK.
Now add another host for the second DMZ Web server.
To add a host for the second DMZ Web server
- In the New Host dialog box, in the Name box, type the
name of Web server 2. In the IP address box, type
10.20.0.2, and then click Add Host.
- In the DNS dialog box informing you that the host record was
successfully created, click OK.
Now add another host for the third DMZ Web server.
To add a host for the third DMZ Web server
- In the New Host dialog box, in the Name box, type the
name of Web server 3. In the IP address box, type
10.20.0.3, and then click Add Host.
- In the DNS dialog box informing you that the host record was
successfully created, click OK.
Now add another host for the Business Desk server in the intranet.
To add a host for the Business Desk server in the intranet
- In the New Host dialog box, in the Name box, type
www. In the IP address box, type 10.30.10.1, and
then click Add Host. This IP address corresponds to the IP
address of the Business Desk server.
- In the DNS dialog box informing you that the host record
www.contoso.com was successfully created, click OK.
- In the New Host dialog box, click Done.
- Close the DNS window.
Creating the Necessary Accounts
After you have configured the intranet DC/DNS server, create the
AFS_Admin_Account account as a member of the Domain Admins group. This
account is used to run Commerce Server and SQL Server services.
To create the AFS_Admin_Account account on the intranet DC/DNS
server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Active Directory Users
and Computers.
- In the Active Directory Users and Computers window, expand
Contoso.com, right-click Users, point to New, and
then click User.
- In the New Object - User dialog box, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| First name |
AFS_Admin_Account |
| User logon name |
AFS_Admin_Account |
- Click Next.
- For Password, type a password for the
AFS_Admin_Account account, in the Confirm password box,
type the password again. Select the check boxes for User cannot
change password and Password never expires, and then click
Next.
- Click Finish.
- In the right pane, right-click Domain Admins, and then click
Properties.
- In the Domain Admins Properties dialog box, on the
Members tab, click Add.
- In the Select Users, Contacts, or Computers dialog box,
select AFS_Admin_Account, click Add, and then click
OK.
- In the Domain Admins Properties dialog box, click
Apply, and then click OK.
- Close the Active Directory Users and Computers window.
Repeat steps 1 through 6 to create the AFS_Service_Account account. The
AFS_Service_Account account will be created as a member of the Domain
Users group, and it will not have administrative privileges. This account
will be used for running BizTalk Messaging Service and AFS COM+
applications.
Joining the Intranet Domain
Now that you have connected each server to the appropriate network and
configured the DC/DNS server, you are ready to join each server to the
domain.
Joining the Business Desk Server to the Intranet Domain
Use the following procedure to join the intranet domain.
To join the Business Desk server to the intranet domain
- On the desktop of the Business Desk server, right-click My
Computer, and then click Properties.
- In the System Properties dialog box, on the Network
Identification tab, click Properties.
- In the Identification Changes dialog box, in the Member
of section, select Domain, type Contoso.com, and then
click OK.
- In the Domain Username and Password dialog box, type
administrator, type the password, and then click OK.
- In the Network Identification dialog box that welcomes you to
the domain, click OK.
- In the Network Identification dialog box that advises you to
restart the computer, click OK.
- In the System Properties dialog box, click OK.
- In the System Settings Change dialog box, click Yes to
restart the computer.
Joining the SQL Server to the Intranet Domain
Use the following procedure to join the intranet domain.
To join the SQL Server to the intranet domain
- On the desktop of the SQL Server, right-click My Computer,
and then click Properties.
- In the System Properties dialog box, on the Network
Identification tab, click Properties.
- In the Identification Changes dialog box, in the Member
of section, select Domain, type Contoso.com, and then
click OK.
- In the Domain Username and Password dialog box, type
administrator, type the corresponding password, and then click
OK.
- In the Network Identification dialog box that welcomes you to
the domain, click OK.
- In the Network Identification dialog box that advises you to
restart the computer, click OK.
- In the System Properties dialog box, click OK.
- In the System Settings Change dialog box, click Yes to
restart the server.
Joining the BizTalk Server to the Intranet Domain
Use the following procedure to join the intranet domain.
To join the BizTalk Server to the intranet domain
- On the desktop of the BizTalk Server, right-click My
Computer, and then click Properties.
- In the System Properties dialog box, on the Network
Identification tab, click Properties.
- In the Identification Changes dialog box, in the Member
of section, select Domain, type Contoso.com, and then
click OK.
- In the Domain Username and Password dialog box, type
administrator, type the corresponding password, and then click
OK.
- In the Network Identification dialog box that welcomes you to
the domain, click OK.
- In the Network Identification dialog box that advises you to
restart the computer, click OK.
- In the System Properties dialog box, click OK.
- In the System Settings Change dialog box, click Yes to
restart the server.
Clustering the Web Servers
After you have set up the Contoso domain and all servers can
communicate properly, you are ready to configure Network Load Balancing on
the DMZ Web cluster.
Configuring Network Load Balancing on the DMZ Web
Cluster
After the network adapters have been configured, you are ready to
configure Network Load Balancing on the Web servers using the following
procedure. This procedure must be completed for each server in the Web
cluster.
To configure Network Load Balancing on each Web server
- On the desktop of the Web server, right-click My Network
Places, and then click Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Public, and then click Properties.
- In the Public Properties dialog box, in the Components
checked are used by this connection section, select the Network
Load Balancing check box, and then click Properties.
- In the Network Load Balancing Properties dialog box, on the
Cluster Parameters tab, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Primary IP address |
10.10.0.10 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Full Internet name |
www.contoso.com |
- In the Network Load Balancing Properties dialog box, on the
Host Parameters tab, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Priority (Unique host ID) |
1 |
| Dedicated IP address |
10.10.0.1 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
- In the Network Load Balancing Properties dialog box, on the
Port Rules tab, select the default port rule (from the list of
rules located at the bottom of the screen) covering ports 0 to 65535,
and then click Remove.
- Create a port rule for port 80 (HTTP over TCP/IP) using the
following information:
| Field |
Enter |
| Port range |
80 to 80 |
| Protocols |
Both |
| Affinity |
None |
- Click OK to return to the Properties dialog box for
the load-balanced network adapter.
- In the Public Properties dialog box, select
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box,
click Advanced.
- In the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box, on the IP
Settings tab, in the IP addresses section, click Add.
- In the TCP/IP Address dialog box, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.10.0.10 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
- Click Add.
- Click OK three times to complete Network Load Balancing
configuration of the load-balanced network adapter.
On Web servers 2 and 3, repeat steps 1 through 14 with the following
exceptions to step 5:
| Cluster member |
Priority (Unique host ID) |
Dedicated IP address |
| Web server 2 |
2 |
10.10.0.2 |
| Web server 3 |
3 |
10.10.0.3 |
Verifying Network Load Balancing Configuration on the DMZ
Web Cluster
After the Web servers have restarted, you can test whether Network Load
Balancing is functioning properly by typing wlbs query in a command
prompt window. You should see the following:
WLBS Cluster Control Utility V2.3. <c> 1997-99 Microsoft Corporation
Host 1 converged as DEFAULT with the following host(s) as part of the cluster:
1, 2, 3
Modifying the Hosts File
Because the Web servers are not part of a domain, you must modify the
hosts file so that Web servers will use the www.contoso.com URL as the VIP
address of the Web servers. You must also resolve the SQL Server and
BizTalk Server names to the intranet ISA Server. By default, the hosts
file is located in the <drive>:\WINNT\system32\drivers\etc
folder. Add the following entry to the hosts file on each Web server:
| 10.10.0.10 |
www.contoso.com |
| 10.20.0.100 |
Type the computer name of the SQL Server,
not the fully qualified domain name. |
| 10.20.0.100 |
Type the computer name of the BizTalk
Server, not fully qualified domain name. |
Installing Solution
Components
This section provides detailed instructions about installing the AFS
solution components. Specifically, this section describes how to:
- Configure the intranet servers.
- Configure the DMZ Web cluster.
- Install Commerce Server 2002.
- Install AFS.
- Configure the external ISA Server.
Setting Up the Intranet Servers
To set up the intranet servers, you will need to install the
appropriate software and configure the following servers:
- SQL Server
- BizTalk Server
- Business Desk
- Intranet ISA Server
Installing and Configuring the SQL Server
This section provides detailed instructions about installing and
configuring Microsoft SQL Server 2000. Specifically, this section
describes how to:
- Install SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition.
- Install Analysis Services.
- Install SQL Server 2000 Service Pack 2.
- Install Analysis Services Service Pack 2.
- Disable named pipes.
- Create the AFSSQL SQL Server account.
Note It is important to
log on as the AFS_Admin_Account user in the Contoso domain.
Installing SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition
Use the following procedure to install SQL Server 2000 Enterprise
Edition.
To install SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition
- Insert the SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition CD into the CD-ROM
drive of the SQL Server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
SQL Server 2000 setup file, and then double-click autorun.exe.
- In the SQL Server 2000 Autorun Menu, select SQL Server
2000 Components.
- In the Install Components screen, select Install Database
Server.
The Microsoft SQL Server Installation Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome screen, click Next.
- In the Computer Name screen, select Local Computer,
and then click Next.
- In the Installation Selection screen, select Create a new
instance of SQL Server, or install Client Tools, and then click
Next.
- In the User Information screen, type a Name and
Company, and then click Next.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and select Yes to proceed with
installation.
- In the CD-Key screen, type the CD-Key, and then click
Next.
- In the Installation Definition screen, select Server and
Client Tools, and then click Next.
- In the Instance Name screen, leave the default values and
click Next.
- In the Setup Type screen, select Typical, accept the
default installation locations, and then click Next.
- In the Services Accounts screen, select Use the same
account for each service, in the Service Settings section,
select Use a Domain User account, and do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Username |
AFS_Admin_Account |
| Password |
The corresponding password. |
| Domain |
Contoso |
- Click Next.
- In the Authentication Mode screen, select Mixed Mode,
type and confirm a password for user sa, and then click
Next.
- In the Start Copying Files screen, click Next.
- In the Choose Licensing Mode screen, in the Licensing
Mode section, select the appropriate number of licenses, and then
click Continue.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Setup Complete screen, click Finish.
Installing Analysis Services
Use the following procedure to install Analysis Services.
To install Analysis Services
- Insert the SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition CD into the CD-ROM
drive of the SQL Server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
SQL Server 2000 Analysis Services setup file, and then double-click
autorun.exe.
- In the SQL Server 2000 Autorun Menu, select SQL Server
2000 Components.
- In the Install Components screen, select Install Analysis
Services.
The Microsoft SQL Server Installation Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome screen, click Next.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and select Yes to proceed with
installation.
- In the Select Components screen, accept the default values,
and click Next.
- In the Data Folder Location screen, click Next.
- In the Select Program Folder screen, click Next.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Setup Complete screen, click Finish.
Installing SQL Server 2000 Service Pack 2
Use the following procedure on the SQL Server to install SQL Server
2000 Service Pack 2 (SP2).
To install SQL Server 2000 SP2
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
SQL Server 2000 SP2 setup file, and then double-click
SQL2KSP2.exe.
- In the Installation Folder screen, use the default
installation path of <drive>:\sql2ksp2, and then
click Finish.
- In the PackageForTheWeb dialog box, click OK.
The SQL2KSP2 files will be extracted to the sql2ksp2 folder.
- In the PackageForTheWeb dialog box, click OK.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the
<drive>:\sql2ksp2 folder, and then double-click
setup.bat.
The SQL Server 2000 SP2 Setup Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome screen, click Next.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and then click Yes to proceed with
installation.
- In the Instance Name screen, click Next.
- In the Connect to Server screen, select Windows
authentication, and then click Next.
- In the Start Copying Files screen, click Next.
- If the Microsoft Data Access Components 2.6 Setup screen
appears, click Next, and then click Finish.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Setup dialog box that advises you to back up your
master and msdb databases, click OK.
- In the Setup Complete screen, click Yes, I want to restart
my computer now, and then click Finish.
Installing Analysis Services Service Pack 2
Use the following procedure to install Analysis Services Service Pack 2
(SP2).
To install Analysis Services SP2
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
SQL Server 2000 Analysis Services SP2 setup file, and then double-click
SQL2KASP2.exe.
- In the Installation Folder screen, type
<drive>:\sql2ksp2olap, and then click Finish.
- In the PackageForTheWeb dialog box, click OK.
The SQL2KSP2 OLAP files will be extracted to the sql2ksp2olap folder.
- In the PackageForTheWeb dialog box, click OK.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the
<drive>:\sql2ksp2olap\msolap\install folder, and then
double-click setup.exe.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Welcome screen, click Next.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and select Yes to proceed with
installation.
- In the Setup Complete screen, click Finish.
Disabling Named Pipes
After installation, disable named pipes and use only TCP/IP as
described in the following procedure. If your setup requires named pipes,
ensure that TCP/IP has a higher precedence than named pipes.
To disable named pipes
- Click Start, and then click Run.
- In the Run dialog box, in the Open box, type
cliconfg, and then click OK.
- In the SQL Server Client Network Utility dialog box, on the
General tab, in the Enabled protocols by order section,
click Named Pipes, click Disable, and then click
OK.
This step moves Named Pipes to the Disabled protocols
list.
Creating the AFSSQL SQL Server Account
Use the following procedure to create the AFSSQL SQL Server
Account.
To create the AFSSQL SQL Server account
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
SQL Server, and then click Enterprise Manager.
- In SQL Server Enterprise Manager, expand Microsoft SQL
Servers, expand SQL Server Group, expand
<servername>, expand Security, and then click
Logins.
- Right-click Logins and then click New Login.
- In the SQL Server Login Properties - New Login dialog box, in
the Name box, type AFSSQL.
- In the Authentication section, click SQL Server
Authentication, in the Password box, type the password for
the AFSSQL user, and then click OK.
- In the Confirm Password dialog box, in the Confirm new
password box, type the password for the AFSSQL user, and then click
OK.
- In the right pane of SQL Server Enterprise Manager, in the
list of users, right-click the newly created AFSSQL user, and then click
Properties.
- In the SQL Server Login Properties - AFSSQL dialog box, in
the Server Roles tab, select the Database Creators check
box.
- In the SQL Server Login Properties - AFSSQL dialog box, on
the Database Access tab, in the Specify which databases can be
accessed by the login box, select the check box for msdb.
- In the Database roles for msdb box, select db_owner,
and then click OK.
Installing and Configuring the BizTalk Server
Note It is important to
log on as the AFS_Admin_Account user in the Contoso domain.
This section provides detailed instructions for configuring the
Microsoft BizTalk Server. This section describes how to:
- Install MSXML 3.0 Service Pack 2.
- Install Message Queuing (also known as MSMQ).
- Verify the Message Queuing installation.
- Install SQL Server 2000 client utilities.
- Install SQL Server 2000 Service Pack 2.
- Disable named pipes.
- Install BizTalk Server 2002 Enterprise Edition.
- Configure the Internet connection.
- Configure proxy settings.
- Set the proper security identity for the XLANG Scheduler.
- Set the proper security identity for the BizTalk Server Interchange
Application.
Installing MSXML 3.0 Service Pack 2
Use the following procedure to install MSXML 3.0 Service Pack 2
(SP2).
To install MSXML 3.0 SP2
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
MSXML 3.0 SP2 installation file, and then double-click
msxml3sp2Setup.exe.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft XML Parser Setup screen,
click Next.
- In the Microsoft XML Parser License Agreement screen, read
the End-User License Agreement (EULA), select I accept the terms in
the License Agreement, and then click Next to proceed with
installation.
- In the Customer Information screen, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
The user name. |
| Organization |
The name of your
organization. |
- Click Next.
- In the Ready to Install screen, click Install.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Completing the Microsoft XML Parser Setup Wizard,
click Finish.
Installing Message Queuing
Install Message Queuing (also known as MSMQ) as its own service, not as
a dependent client. Use the following procedure on the BizTalk Server to
install Message Queuing with the Windows 2000 Configure Your Server
utility. During this installation process, you will be prompted to insert
the Windows 2000 Advanced Server CD into the CD-ROM drive.
To install Message Queuing with the Windows 2000 Configure Your
Server utility
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Configure Your
Server.
- In the Windows 2000 Configure Your Server
dialog box, in the left column, expand Advanced, and then select
Message Queuing.
- In the right pane, click Start to start the Message Queuing
Installation Wizard.
- In the Welcome to the Message Queuing Installation Wizard
screen, click Next.
- In the Message Queuing Type screen, select Message Queuing
server, ensure that the Enable routing and Manually select
access mode to Active Directory boxes are not selected, and then
click Next.
- In the Message Queuing Server screen, select Message
Queuing will not access a directory service, and then click
Next.
- In the Completing the Message Queuing Installation Wizard
screen, click Finish.
Verifying the Message Queuing Installation
After completing the Message Queuing Installation Wizard, you must
verify that Message Queuing was installed properly and that all required
subdirectories exist.
To verify the Message Queuing installation
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the Computer Management screen, expand Services and
Applications, expand Message Queuing, and then select
Private Queues.
- In the details pane, verify that the following four private queues
exist:
- admin_queue$
- mqis_queue$
- notify_queue$
- order_queue$
Installing SQL Server 2000 Client Utilities
Because a separate SQL Server exists, only the SQL Server 2000 client
utilities need to be installed on the BizTalk Server.
To install the SQL Server 2000 client utilities
- Insert the SQL Server 2000 CD into the CD-ROM drive of the BizTalk
Server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
SQL Server 2000 setup file, and then double-click autorun.exe.
- In the SQL Server 2000 Autorun Menu, click SQL Server 2000
Components.
- In the Install Components screen, select Install Database
Server.
The SQL Server Installation Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft SQL Server Installation
Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the Computer Name screen, select Local Computer,
and then click Next.
- In the Installation Selection screen, select Create a new
instance of SQL Server, or install Client Tools, and then click
Next.
- In the User Information screen, in the Name box, type
your name, in the Company box, type the name of your company, and
then click Next.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and then click Yes to proceed with
installation.
- In the CD-Key screen, type the CD-Key, and then click
Next.
- In the Installation Definition screen, select Client Tools
Only, and then click Next.
- In the Select Components screen, click Next.
- In the Start Copying Files screen, click Next.
This step starts the SQL Server installation process.
- In the Setup Complete screen, click Finish. If Setup
prompts you to restart the server, click Yes.
Installing SQL Server 2000 Service Pack 2
After installing SQL Server 2000 client utilities, you need to install
SQL Server 2000 Service Pack 2 (SP2) on the BizTalk Server.
To install SQL Server 2000 SP2
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
SQL Server 2000 SP2 setup file, and then double-click
SQL2KSP2.exe.
- In the Installation Folder screen, use the default
installation path of <drive>:\sql2ksp2, and then
click Finish.
- In the PackageForTheWeb dialog box, click OK.
The SQL2KSP2 files will be extracted to the sql2ksp2 folder.
- In the PackageForTheWeb dialog box, click OK.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
SQL Server 2000 SP2 setup file, and then double-click setup.bat.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Service Pack 2
Installation Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and then click Yes to proceed with
installation.
- In the Start Copying Files screen, click Next.
- In the Setup Complete screen, click Yes, I want to restart
my computer now, and then click Finish.
Disabling Named Pipes
After installation, disable named pipes and use only TCP/IP as
described in the following procedure. If your setup requires named pipes,
ensure that TCP/IP has a higher precedence than named pipes.
To disable named pipes
- Click Start, and then click Run.
- In the Run dialog box, in the Open box, type
cliconfg, and then click OK.
- In the SQL Server Client Network Utility dialog box, on the
General tab, in the Enabled protocols by order section,
click Named Pipes, click Disable, and then click
OK.
This step moves Named Pipes to the Disabled protocols
list.
Installing BizTalk Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
Use the following procedure to install BizTalk Server 2002 Enterprise
Edition.
To install BizTalk Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
- Insert the BizTalk Server 2002 Enterprise Edition CD into the CD-ROM
drive.
The Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002 screen is displayed.
- In the Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002 screen, select
Install Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002.
The Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002 Setup Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002 Setup
Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the License Agreement screen, read the End-User License
Agreement, select I accept this agreement to proceed with
installation, and then click Next.
- In the Customer Information screen, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
The user name. |
| Organization |
The name of your
organization. |
- In the Destination Folder screen, use the default
installation location, and click Next.
- In the Setup Type screen, select Complete, and then
click Next.
- In the Configure BizTalk Server Administrative Access screen,
accept the default values, and then click Next.
- In the Microsoft BizTalk Server Service Log On Properties
screen, select This account, and do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
Contoso\AFS_Service_Account |
| Password |
The corresponding
password. |
- Ensure that the check box for Start service after setup
completes is selected, and then click Next.
- In the Ready To Install the Program screen, ensure that all
components will be installed, and then click Install.
Note It is OK to ignore
the warning that informs you that BizTalk Orchestration Designer will
not run because it requires Microsoft Visio 2002. Visio can be
installed on development and testing platforms, but is not required
for this deployment.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002 Messaging
Database Setup Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the Configure a BizTalk Messaging Management Database
screen, select Create a new BizTalk Messaging Management
database, and do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Server name |
The computer name of the SQL
Server. |
| Database |
InterchangeBTM |
- Click Next.
- In the Configure a BizTalk Server Group screen, select
Create a new BizTalk Server group, in the Group name box,
type BizTalk Server Group, and then click Next.
- In the Configure a Tracking Database screen, select Create
a new Tracking database, and do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Server name |
The computer name of the SQL
Server. |
| Database |
InterchangeDTA |
- Click Next.
- In the Configure a Shared Queue Database screen, select
Create a new Shared Queue database, and do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Server name |
The computer name of the SQL
Server. |
| Database |
InterchangeSQ |
- Click Next.
- In the Verify BizTalk Server Group screen, verify the
information, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002 Messaging
Database Setup Wizard screen, click Finish.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002 Orchestration
Persistence Database Server Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the Configure a default Orchestration Persistence Database
screen, select Create a new default Orchestration Persistence
database, and do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Server name |
The computer name of the SQL
Server. |
| Database |
XLANG |
- Click Finish.
- In the Completing the Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002 Setup
Wizard screen, click Finish.
- Restart the server.
Configuring the Internet Connection
Use the following procedure to configure the Internet connection.
To configure the Internet connection
- On the desktop of the BizTalk Server, double-click Connect to the
Internet.
- In the Welcome to the Internet Connection Wizard screen,
select the LAN option, and then click Next.
- In the Setting up your Internet Connection screen, select the
LAN option, and then click Next.
- In the Local Area Network Internet Configuration screen,
clear all check boxes, and then click Next.
- In the Set Up your Internet Mail Account screen, select
No, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the Internet Connection Wizard screen,
click Finish.
Configuring Proxy Settings
For the BizTalk Server to access the Internet, you must configure the
proxy settings in Internet Explorer as described in the following
procedure.
To configure proxy settings
- In Internet Explorer, on the Tools menu, click
Internet Options.
- In the Internet Options dialog box, on the Connections
tab, in the Local Area Network (LAN) settings section, click
LAN Settings.
- In the Local Area Network (LAN) Settings dialog box, in the
Proxy server section, select Use a proxy server, in the
Address box, type 10.30.0.100, and in the Port box,
type 8080. Select Bypass proxy server for local addresses,
and then click OK.
- In the Internet Options dialog box, click OK.
Setting the Proper Security Identity for the XLANG Scheduler
Configure the XLANG Scheduler to run under the AFS_Service_Account.
To set proper security identity for running the XLANG Scheduler on
the BizTalk Server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Component Services.
- In the Component Services window, expand Component
Services, expand Computers, expand My Computer, expand
COM+ Applications, right-click XLANG Scheduler, and then
click Properties.
- In the XLANG Scheduler Properties dialog box, on the
Advanced tab, clear the check box for Disable Changes, and
then click OK.
- In the Warning dialog box that asks for confirmation, click
Yes.
- Right-click XLANG Scheduler again, and then click
Properties.
- In the XLANG Scheduler Properties dialog box, on the
Identity tab, select This user, and do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User |
Contoso\AFS_Service_Account |
| Password |
The corresponding password. |
| Confirm Password |
The corresponding
password. |
- On the Advanced tab, select Disable Changes, and then
click OK.
- In the Warning dialog box asking for confirmation, click
Yes.
Setting the Proper Security Identity for the BizTalk Server
Interchange Application
Configure the BizTalk Server Interchange Application to run under the
AFS_Service_Account.
To set proper security identity for running the BizTalk Server
Interchange Application on the BizTalk Server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Component Services.
- In the Component Services window, expand Component
Services, expand Computers, expand My Computer, expand
COM+ Applications, right-click BizTalk Server Interchange
Application, and then click Properties.
- In the BizTalk Server Interchange Application Properties
dialog box, on the Advanced tab, clear the check box for
Disable Changes, and then click OK.
- In the Warning dialog box that asks for confirmation, click
Yes.
- Right-click BizTalk Server Interchange Application
again, and then click Properties.
- In the BizTalk Server Interchange Application
Properties dialog box, on the Identity tab, select This
user, and do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User |
Contoso\AFS_Service_Account |
| Password |
The corresponding password. |
| Confirm Password |
The corresponding
password. |
- On the Advanced tab, select Disable Changes, and then
click OK.
- In the Warning dialog box asking for confirmation, click
Yes.
Installing and Configuring the Business Desk Server
This section provides detailed instructions for configuring the
intranet Business Desk server. Specifically, this section describes how
to:
- Install MSXML 3.0 Service Pack 2.
- Install Internet Explorer 5.5 Service Pack 2.
- Install Analysis Services.
- Install Analysis Services Service Pack 2.
- Install the Microsoft .NET Framework.
- Install MDAC 2.7.
- Install MDAC 2.7 Rollup.
- Install Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5.
- Install MSXML 4.0.
- Install Message Queuing (also known as MSMQ).
- Verify the Message Queuing installation.
- Disable named pipes.
- Create a new Web site for Business Desk.
- Maximize Web server performance.
- Configure the Internet connection.
- Configure proxy settings.
Note It is important to
log on as the AFS_Admin_Account user in the Contoso domain.
Installing MSXML 3.0 Service Pack 2
Use the following procedure to install MSXML 3.0 Service Pack 2
(SP2).
To install MSXML 3.0 SP2
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
MSXML 3.0 SP2 installation file, and double-click
msxml3sp2Setup.exe.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft XML Parser Setup Wizard
screen, click Next.
- In the End-user License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), select I accept the terms in the License
Agreement, and then click Next to proceed with installation.
- In the Customer Information screen, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
The user name. |
| Organization |
The name of your
organization. |
- Click Next.
- In the Ready to Install screen, click Install.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Completing the Microsoft XML Parser Setup Wizard
screen, click Finish.
Installing Internet Explorer 5.5 Service Pack 2
Use the following procedure to install Internet Explorer 5.5 Service
Pack 2 (SP2).
To install Internet Explorer 5.5 SP2
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
Internet Explorer 5.5 SP2 setup file, and then double-click
ie5setup.exe.
- In the Welcome to Setup for Internet Explorer and Internet
Tools screen, read the End-User License Agreement (EULA), select
I accept the agreement, and then click Next to proceed
with installation.
- In the Windows Update: Internet Explorer and Internet Tools
screen, click Next.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Restart Computer screen, click Finish.
Installing Analysis Services
Use the following procedure to install Analysis Services on the
Business Desk server.
To install Analysis Services
- Insert the SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition CD into the CD-ROM
drive of the Business Desk server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
SQL Server 2000 Analysis Services setup file, and then double-click
autorun.exe.
- In the SQL Server 2000 Autorun Menu, select SQL Server
2000 Components.
- In the Install Components screen, select Install Analysis
Services.
The Microsoft SQL Server Installation Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome screen, click Next.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and then click Yes to proceed with
installation.
- In the Select Components screen, accept the default values,
and click Next.
- In the Data Folder Location screen, click Next.
- In the Select Program Folder screen, click Next.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Setup Complete screen, click Finish.
Installing Analysis Services Service Pack 2
Use the following procedure to install Analysis Services Service Pack 2
(SP2).
To install Analysis Services SP2
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
SQL Server 2000 Analysis Services SP2 setup file, and then double-click
SQL2KASP2.exe.
- In the Installation Folder screen, type
<drive>:\sql2ksp2olap, and then click Finish.
- In the PackageForTheWeb dialog box, click OK.
The SQL2KSP2 OLAP files will be extracted to the sql2ksp2olap folder.
- In the PackageForTheWeb dialog box, click OK.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the
<drive>:\sql2ksp2olap\msolap\install folder, and then
double-click setup.exe.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Welcome screen, click Next.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and then click Yes to proceed with
installation.
- In the Setup Complete screen, click Finish.
Installing the .NET Framework
Use the following procedure on the Business Desk server to install the
.NET Framework.
To install the .NET Framework
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
.NET Framework setup file, and then double-click dotnetfx.exe.
- In the Microsoft .NET Framework Setup dialog box asking if
you want to install the .NET Framework, click Yes.
- In the Microsoft .NET Framework Setup dialog box asking if
you want to update Microsoft Windows Installer components, click
Yes.
- In the Microsoft .NET Framework (English) Setup screen, click
Next.
This step starts the .NET Framework installation process.
- In the Microsoft .NET Framework (English) Setup dialog box,
click OK.
- In the System Settings Change screen, click Yes to
restart the server.
Installing MDAC 2.7
Use the following procedure on the Business Desk server to install MDAC
2.7.
To install MDAC 2.7 on the Business Desk server
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
MDAC 2.7 setup file, and then double-click MDAC_TYP.exe.
- In the End User License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), select I accept all of the terms of the
preceding license agreement to proceed with installation, and then
click Next.
- In the Microsoft Data Access Components 2.7 Setup screen,
click Finish.
This step starts the MDAC 2.7 installation process.
- In the Microsoft Data Access Components 2.7 Setup screen,
click Close.
Note Installing MDAC 2.7
may fail on the first attempt. Reinstall if necessary.
Installing MDAC 2.7 Rollup
Use the following procedure on the Business Desk server to install the
MDAC 2.7 Rollup.
To install the MDAC 2.7 Rollup on the Business Desk server
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
MDAC 2.7 Rollup setup file, and then double-click
CS_MDAC27_x86_en.exe.
- In the Microsoft Data Access Components Hotfix Installer
screen, click OK.
This step starts the MDAC 2.7 Rollup installation process.
- In the Setup is complete dialog box, click OK.
- In the System Settings Change screen, click Yes to
restart the server.
Installing Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5
Use the following procedure on the Business Desk server to install
Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5 (SP5).
To install Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime SP5 on the Business Desk
server
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime SP5 setup file, and then double-click
VBRun60sp5.exe.
- In the Visual Basic 6.0 with Visual Studio 6.0 Service Pack 5 Run
Time Files dialog box, click Yes to install the Visual Basic
6.0 run time files.
This step starts the Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5
installation process.
Note No dialog box will
appear to indicate that installation has completed.
Installing MSXML 4.0
Use the following procedure on the Business Desk server to install
Microsoft XML Core Services (MSXML) 4.0.
To install MSXML 4.0
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
MSXML 4.0 installation file, and then double-click msxml4.msi.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft XML Parser and SDK Setup
Wizard, click Next.
- In the End-User License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), select I accept the terms in the License
Agreement, and then click Next to proceed with installation.
- In the Customer Information screen, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
The user name. |
| Organization |
The name of your
organization. |
- Click Next.
- In the Choose Setup Type screen, click Install Now.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Completing the Microsoft XML Parser and SDK Setup
Wizard, click Finish.
Installing Message Queuing
Use the following procedure on the Business Desk server to install
Message Queuing. This procedure may require you to insert the Windows 2000
Advanced Server CD into the CD-ROM drive.
To install Message Queuing on the Business Desk server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Configure Your
Server.
- In the Windows 2000 Configure Your Server screen, expand
Advanced in the left column, and then click Message
Queuing.
- In the right pane, click Start to start the Message Queuing
Installation Wizard.
The Message Queuing Installation Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the Message Queuing Installation Wizard
screen, click Next.
- In the Message Queuing Type screen, select Message Queuing
server, ensure that the Enable routing and Manually select
access mode to Active Directory boxes are not selected, and then
click Next.
- In the Message Queuing Server screen, select Message
Queuing will not access a directory service, and then click
Next.
- In the Completing the Message Queuing Installation Wizard
screen, click Finish.
Verifying Message Queuing Installation
After completing the Message Queuing Installation Wizard, you must
verify that Message Queuing was installed properly and that all required
subdirectories exist.
To verify the Message Queuing installation
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the Computer Management window, expand Services and
Applications, expand Message Queuing, and then click
Private Queues.
- In the right pane, verify that the following four private queues
exist:
- admin_queue$
- mqis_queue$
- notify_queue$
- order_queue$
Disabling Named Pipes
After installation, disable named pipes and use only TCP/IP as
described in the following procedure.
To disable named pipes
- Click Start, and then click Run.
- In the Run dialog box, in the Open box, type
cliconfg, and then click OK.
- In the SQL Server Client Network Utility dialog box, on the
General tab, if you have the Default network library
section, select TCP/IP from the drop-down list, and then click
OK.
–Or–
If you have a Disabled Protocols section, select
TCP/IP, and then click Enabled. If Named Pipes
appears in the Enabled protocols section, click Named
Pipes, click Disable, and then click OK.
Creating a New Web Site for the Business Desk Server
To avoid potential security risks associated with Internet Services
Application Programming Interface (ISAPI) and the default Web site, you
need to create a new Web site on the Business Desk server. First, you need
to create a folder to hold the AFS Web site files, and then you need to
create the new AFS Web site.
To create a folder to contain the files for the new Web site for the
Business Desk server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Accessories, and then click Windows Explorer.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the root drive.
- On the File menu, click New, and then click
Folder.
- In the right pane, in the new folder Name box, type
MySite, and then press ENTER.
Now that you have created a folder to contain the files for the new Web
site, you are ready to create the new Web site.
To create the new Web site for the Business Desk server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the Computer Management window, expand Services and
Applications, expand Internet Information Services,
right-click Default Web Site, and then click Stop.
- Right-click Internet Information Services, point to
New, and then click Web Site.
The Web Site Creation Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the Web Site Creation Wizard screen, click
Next.
- In the Web Site Description screen, type MySite as the
description for the new Web site, and then click Next.
- In the IP Address and Port Settings screen, accept the
default values and click Next.
- In the Web Site Home Directory screen, type the path to the
MySite folder, or click Browse to navigate to this folder.
- Ensure that the check box for the option Allow anonymous access
to this Web site is selected, and then click Next.
- In the Web Site Access Permissions screen, accept the default
values and click Next.
- In the You have successfully completed the Web Site Creation
Wizard screen, click Finish.
Maximizing Web Server Performance
You can maximize the performance of the Business Desk server by
increasing the Performance Tuning setting.
To increase the Performance Tuning setting
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Services
Manager.
- In the Internet Information Services screen, expand
<servername>, right-click MySite, and then
click Properties.
- In the MySite Properties dialog box, on the
Performance tab, in the Performance tuning section,
increase the setting to More than 100,000, and then click
OK.
Configuring the Internet Connection
Use the following procedure to configure the Internet connection.
To configure the Internet connection
- On the desktop of the Business Desk server, double-click Connect
to the Internet.
- In the Welcome to the Internet Connection Wizard screen,
select the LAN option, and then click Next.
- In the Setting up your Internet Connection screen, select the
LAN option, and then click Next.
- In the Local Area Network Internet Configuration screen,
clear all check boxes, and then click Next.
- In the Set Up your Internet Mail Account screen, select
No, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the Internet Connection Wizard screen,
click Finish.
Configuring Proxy Settings
For the Business Desk server to access the Internet, you must configure
the proxy settings in Internet Explorer as described in the following
procedure.
To configure proxy settings
- In Internet Explorer, on the Tools menu, click
Internet Options.
- In the Internet Options dialog box, on the Connections
tab, in the Local Area Network (LAN) settings section, click
LAN Settings.
- In the Local Area Network (LAN) Settings dialog box, in the
Proxy server section, select Use a proxy server, in the
Address box, type 10.30.0.100, and in the Port box,
type 8080. Do not select Bypass proxy server for local
addresses, and then click OK.
- In the Internet Options dialog box, click Apply, and
then click OK.
Installing and Configuring the Intranet ISA Server
This section provides detailed instructions for configuring Microsoft
Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server 2000 in the intranet. In
addition to the instructions for installing and configuring ISA Server,
this section describes how to modify ISA Server properties so that it will
function properly with AFS in the medium deployment. Specifically, this
section describes how to:
- Remove Internet Information Services (IIS).
- Install ISA Server Standard Edition.
- Install ISA Server Service Pack 1.
- Install Windows 2000 Hotfix Q315764.
- Add incoming Web request listeners.
- Create a new protocol definition for Message Queuing (also known as
MSMQ).
- Create a new site and content rule.
- Create client address sets.
- Create new protocol rules.
- Create Web publishing rules.
- Create server publishing rules.
- Create destination sets.
- Create new routing rules.
- Enable IP packet filtering.
- Maximize ISA Server performance.
- Modify the hosts file.
Removing Internet Information Services
If you installed Internet Information Services (IIS) by default on the
intranet ISA Server when you installed Windows 2000, you can remove it
because it is not needed.
To remove IIS from the intranet ISA Server
- Click Start, point to Settings, and then click
Control Panel.
- In the Control Panel window, double-click Add/Remove
Programs.
- In the Add/Remove Programs dialog box, click Add/Remove
Windows Components from the left column.
The Windows Components Wizard starts.
- In the Windows Components screen, clear the check box next to
the option Internet Information Services (IIS), and then click
Next. You might have to scroll down to view the Internet
Information Services (IIS) component.
- If the Terminal Services Setup screen appears, select
Remote administration mode, and then click Next. The
wizard might take a few minutes to complete.
- In the Completing the Windows Components Wizard screen, click
Finish. IIS is now uninstalled.
- Click Close to exit Add/Remove Programs.
Installing ISA Server Standard Edition
After you have removed IIS, you can install ISA Server Standard
Edition.
To install ISA Server Standard Edition
- Insert the ISA Server 2000 Standard Edition CD into the CD-ROM drive
of the intranet ISA Server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
ISA Server 2000 setup file, and then double-click ISAAutorun.exe.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server Setup screen, click Install
ISA Server.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server (Standard Edition) Setup dialog
box, click Continue.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server Setup dialog box, read the
End-User License Agreement (EULA), and then click I Agree to
accept the terms of the EULA to proceed with installation.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server (Standard Edition) Setup dialog
box, click Full Installation.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server Setup dialog box, select
Integrated mode, and then click Continue.
- In the Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server
Setup dialog box, click OK to accept the default location and
size for the ISA Server cache drives.
- In the Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server
Setup dialog box for entering the IP address ranges, click
Construct Table.
- In the Local Address Table dialog box, clear the check box
for the option Add the following private ranges, select Add
address ranges based on the Windows 2000 Routing Table, ensure that
the only IP address selected is that of the Private network adapter
(10.30.0.100), and then click OK.
- In the Setup Message dialog box, click OK.
- In the Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server
Setup dialog box for entering the IP address ranges, click
OK.
- If a message box appears informing you that Message Screener
requires the SMTP Service, click OK.
The ISA Server installation starts.
- In the Launch ISA Management Tool dialog box, clear the check
box for starting up the wizard, and then click OK.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server (Standard Edition) Setup dialog
box that states that ISA Server Setup was completed successfully, click
OK.
Installing ISA Server Service Pack 1
After you have installed ISA Server, you can install ISA Server Service
Pack 1 (SP1).
To install ISA Server SP1
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
ISA Server SP1 setup file, and then double-click ISASP1.exe.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and select I agree to proceed with
installation.
This step starts the ISA Server Service Pack 1 installation process.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server 2000 Update Setup dialog box,
click OK.
- The server will restart after the Service Pack has been installed.
Installing Windows 2000 Hotfix Q315764
Use the following procedure to install Windows 2000 Hotfix Q315764.
To install Windows 2000 Hotfix Q315764
- In Internet Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321828 and follow the online installation
instructions.
Adding Incoming Web Request Listeners
Because ISA Server intercepts requests from the DMZ for servers on the
intranet, you must specify which IP addresses will listen for Web requests
from the DMZ.
To add incoming Web request listeners
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, right-click <servername>, and then click
Properties.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog box, on
the Incoming Web Requests tab, click Add.
- In the Add/Edit Listeners dialog box, in the Server
drop-down list, select <servername>.
- In the IP Address drop-down list, select the IP address
corresponding to the Public network adapter. The example IP
address used in this document is 10.20.0.100.
- Confirm that all check boxes are cleared except for
Integrated, click OK, and then click Apply.
- In the ISA Server Warning dialog box, select Save the
changes and restart the service(s), and then click OK.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog
box, click Add.
- In the Add/Edit Listeners dialog box, in the Server
drop-down list, select <servername>.
- In the IP Address drop-down list, select the IP address
corresponding to the Dedicated ISA network adapter. The example
IP address used in this document is 10.50.0.100.
- Confirm that all check boxes are cleared except for
Integrated, and then click OK.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog box, click
Apply.
- In the ISA Server Warning dialog box, select Save the
Changes and Restart the service(s), and then click OK.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog box, click
OK.
Creating a New Protocol Definition for Message Queuing
Protocol definitions specify the low-level protocols and port numbers
that connections use. You need to create two new protocol definitions
named MSMQ Inbound and MSMQ Outbound to support the server publishing rule
and protocol rule. Use the following procedures to create these two new
protocol definitions that will define the Message Queuing port.
To create the new protocol definition named MSMQ Inbound
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and Arrays, expand
<servername>, expand Policy Elements, right-click
Protocol Definitions, click New, and then click Definition.
The New Protocol Definition Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Protocol Definition Wizard screen,
in the Protocol definition name box, type MSMQ Inbound,
and then click Next.
- In the Primary Connection Information screen, in the Port
number box, type 1801, in the Protocol type section,
select TCP, in the Direction section, select
Inbound, and then click Next.
- In the Secondary Connections screen, select No, and
then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Protocol Definition Wizard screen,
click Finish.
After you have created the inbound rule, you are ready to create the
outbound rule.
To create the new protocol definition named MSMQ Outbound
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and Arrays, expand
<servername>, expand Policy Elements, right-click
Protocol Definitions, click New, and then click Definition.
The New Protocol Definition Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Protocol Definition Wizard screen,
in the Protocol definition name box, type MSMQ Outbound,
and then click Next.
- In the Primary Connection Information screen, in the Port
number box, type 1801, in the Protocol type section,
select TCP, in the Direction section, select
Outbound, and then click Next.
- In the Secondary Connections screen, select No, and
then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Protocol Definition Wizard screen,
click Finish.
Creating a New Site and Content Rule
Site and content rules determine if and when specified users can access
content on specific destination sets. Use the following procedure to
create a new site and content rule.
To create a new site and content rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and Arrays, expand
<servername>, expand Access Policy, right-click Site
and Content Rules, click New, and then click Rule.
The New Site and Content Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Site and Content Rule Wizard
screen, in the Site and content rule name box, type Allow,
and then click Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, select Allow, and then
click Next.
- In the Rule Configuration screen, select Allow access
based on destination, and then click Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, from the drop-down list,
select All destinations, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Site and Content Rule Wizard
screen, click Finish.
Creating Client Address Sets
Client address sets consist of one or more computers. For access policy
rules, client address sets include computers that are part of your
internal network. For Web publishing rules, client address sets include
computers external to your network.
You will need to create three client address sets: Business Desk
server, BizTalk Server, and Web servers. The client address sets will be
used by either a protocol or a publishing rule.
Use the following procedure to create the client address set named
BizTalk Server.
To create the client address set named BizTalk Server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Policy
Elements, right-click Client Address Sets, click New,
and then click Set.
- In the Client Set screen, in the Name box, type
BizTalk Server, and then click Add.
- In the Add/Edit IP Addresses screen, in the From
field, type 10.30.0.1, in the To field, type
10.30.0.1, and then click OK.
- In the Client Set screen, click OK.
Use the following procedure to create the client address set named
Business Desk server.
To create the client address set named Business Desk server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Policy
Elements, right-click Client Address Sets, click New,
and then click Set.
- In the Client Set screen, in the Name box, type
Business Desk server, and then click Add.
- In the Add/Edit IP Addresses screen, in the From
field, type 10.30.10.1, in the To field, type
10.30.10.1, and then click OK.
- In the Client Set screen, click ADD.
- In the Add/Edit IP Addresses screen, in the From box,
type 10.30.30.1, in the To box, type 10.30.30.1,
and then click OK.
Note The IP address
10.30.30.1 is the IP address of the Business Desk client that you will
build later in this guide. If you need to add additional Business Desk
clients, be sure to add their IP addresses to this Business Desk
server client address set.
- In the Client Set screen, click OK.
Use the following procedure to create the client address set named Web
servers.
To create the client address set named Web servers
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Policy
Elements, right-click Client Address Sets, click New,
and then click Set.
- In the Client Set screen, in the Name box, type Web
Servers, and then click Add.
- In the Add/Edit IP Addresses screen, in the From
field, type 10.20.0.1, in the To field, type
10.20.0.3, and then click OK.
- In the Client Set screen, click OK.
Creating New Protocol Rules
Protocol rules determine which protocols clients can use and when.
Use the following procedure to create the MSMQ Outbound protocol
rule.
To create the MSMQ Outbound protocol rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Access
Policy, right-click Protocol Rules, click New, and
then click Rule.
The New Protocol Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Protocol Rule Wizard screen, in the
Protocol rule name box, type MSMQ Outbound, and then click
Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, select Allow, and then
click Next.
- In the Protocols screen, ensure that Selected
protocols is selected from the drop-down list. In the
Protocols section, ensure that MSMQ Outbound and Show
only selected protocols are selected, and then click Next.
- In the Schedule screen, from the drop-down list, select
Always, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, select Specific computers
(client address sets), and then click Next.
- In the Client Sets screen, click Add.
- In the Add Client Sets dialog box, in the Defined Sets
section, double-click BizTalk Server, and then click OK.
- In the Client Sets screen, click Next.
- In the Completing the New Protocol Rule Wizard screen, click
Finish.
Use the following procedure to create the Web Outbound protocol
rule.
To create the Web Outbound protocol rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Access
Policy, right-click Protocol Rules, click New, and
then click Rule.
The New Protocol Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Protocol Rule Wizard screen, in the
Protocol rule name box, type Web Outbound, and then click
Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, select Allow, and then
click Next.
- In the Protocols screen, ensure that Selected
protocols is selected from the drop-down list. In the
Protocols section, ensure that HTTP, HTTPS, and
Show only selected protocols are selected, and then click
Next.
- In the Schedule screen, from the drop-down list, select
Always, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, select Specific computers
(client address sets), and then click Next.
- In the Client Sets screen, click Add.
- In Add Client Sets dialog box, in the Defined Sets
section, double-click BizTalk Server, double-click Business
Desk server, and then click OK.
- In Client Sets screen, click Next.
- In the Completing the New Protocol Rule Wizard screen, click
Finish.
Creating Web Publishing Rules
Web publishing rules define how incoming Web requests are handled. You
need to create a new Web publishing rule to redirect HTTP requests from
the DMZ to the Business Desk server and BizTalk Server in the
intranet.
Note It is important that
the rules be listed in the following order: BizTalk Server Requests,
Business Desk Requests, and Default. The order of the rules can be set
by using the UP or DOWN arrow in the ISA Management window.
To create the Web publishing rule: Business Desk Requests
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand
Publishing, right-click Web Publishing Rules, click
New, and then click Rule.
The New Web Publishing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
in the Web publishing rule name box, type Business Desk
Requests, and then click Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, from the drop-down list,
select All destinations, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, select Any Request, and
then click Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, select Redirect the request to
this internal Web server (name or IP address), and then type the IP
address of the Business Desk server in the text box next to the
Browse button. The example IP address used in this document is
10.30.10.1.
- Select Send the original host header to the publishing
server, use the default ports, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
click Finish.
To create the Web publishing rule: BizTalk Server Requests
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand
Publishing, right-click Web Publishing Rules, click
New, and then click Rule.
The New Web Publishing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
in the Web publishing rule name box, type BizTalk Server
Requests, and then click Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, from the drop-down list,
select All destinations, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, select Specific Computers
(client address sets), and then click Next.
- In the Client Sets screen, click Add.
- In the Add Client Sets screen, in the Client Sets
field, double-click Web Servers, and then click OK.
- In the Client Sets screen, click Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, select Redirect the request to
this internal Web server (name or IP address), and then type the IP
address of the BizTalk Server in the text box next to the Browse
button. The example IP address used in this document is
10.30.0.1.
- Select Send the original host header to the publishing
server, use the default ports, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
click Finish.
- Verify that the BizTalk Server Requests rule appears as the
first rule in the ISA Management console. If it is not, select the rule,
and then click the Up Arrow.
Creating Server Publishing Rules
A server publishing rule maps incoming requests to the appropriate
internal server. Use the following procedure to create the SQL Server
publishing rule.
To create the SQL Server publishing rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and Arrays, expand
<servername>, expand Publishing, right-click Server
Publishing Rules, click New, and then click Rule.
The New Server Publishing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Server Publishing Rule Wizard
screen, in the Server publishing rule name box, type SQL,
and then click Next.
- In the Address Mapping screen, in the IP address of
internal server box, type the IP address of the SQL Server. The
example IP address used in this document is 10.30.20.1.
- In the Address Mapping screen, in the External IP address
on ISA Server box, type the IP address of the ISA Server that is
used by the Web cluster in the DMZ. The example IP address used in this
document is 10.20.0.100.
- Click Next.
- In the Protocol Settings screen, from the drop-down list,
select Microsoft SQL Server, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, select Any request, and
then click Next.
- In the Complete the New Server Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
click Finish.
Now that you have created the SQL Server publishing rule, you are ready
to create the Message Queuing server publishing rule.
To create the Message Queuing server publishing rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and Arrays, expand
<servername>, expand Publishing, right-click Server
Publishing Rules, click New, and then click Rule.
The New Server Publishing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Server Publishing Rule Wizard
screen, in the Server publishing rule name box, type MSMQ,
and then click Next.
- In the Address Mapping screen, in the IP address of
internal server box, type the IP address of the BizTalk Server. The
example IP address used in this document is 10.30.0.1.
- In the External IP address on ISA Server box, type the IP
address of the ISA Server that is used by the DMZ Web cluster. The
example IP address used in this document is 10.20.0.100.
- Click Next.
- In the Protocol Settings screen, from the drop-down list,
select MSMQ Inbound, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, select Any request, and
then click Next.
- In the Complete the New Server Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
click Finish.
Creating Destination Sets
A destination set is defined as a set of path locations or a specific
IP range. Destination sets are used by routing or publishing rules to
define a specific set of destinations. Use the following procedure to
create a destination set for the Web servers.
To create a destination set for the Web servers
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Policy
Elements, right-click Destination Sets, click New, and
then click Set.
- In the New Destination Set dialog box, in the Name
box, type Web Farm Catalogs, and then click Add.
- In the Add/Edit Destination dialog box, select
Destination, type *.contoso.com, and then click OK.
- In the New Destination Set dialog box, click OK.
Creating New Routing Rules
Routing rules determine whether a client's Web request is retrieved
directly, routed to an upstream ISA Server, or routed to an alternative
destination. Use the following procedure to create the Web Farm Catalogs
Refresh routing rule. This rule applies to the Web servers and uses the
Web Farm Catalogs destination set.
To create the Web Farm Catalogs Refresh routing rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Network
Configuration, right-click Routing, click New, and
then click Rule.
The New Routing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Routing Rule Wizard screen, in the
Routing rule name box, type Web Farm Catalogs Refresh, and
then click Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, from the drop-down list,
select Specified Destination Set, from the drop-down list next to
Name, select Web Farm Catalogs, and then click
Next.
- In the Request Action screen, select Retrieve them
directly from specified destination, and then click Next.
- In the Cache Retrieval Configuration screen, select A
valid version of the object, and then click Next.
- In the Cache Content Configuration screen, select If
source and request headers indicate to cache, then the content will be
cached, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Routing Rule Wizard screen, click
Finish.
After you have created the Web Farm Catalogs Refresh routing rule, you
are ready to create the Inbound routing rule for internal domain requests.
Use the following procedure to create this routing rule.
To create the Inbound routing rule for internal domain requests
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Network
Configuration, right-click Routing, click New, and
then click Rule.
The New Routing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Routing Rule Wizard screen, in the
Routing rule name box, type Inbound, and then click
Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, from the drop-down list,
select All internal destinations, and then click Next.
- In the Request Action screen, select Retrieve them
directly from specified destination, and then click Next.
- In the Cache Retrieval Configuration screen, select A
valid version of the object, and then click Next.
- In the Cache Content Configuration screen, select If
source and request headers indicate to cache, then the content will be
cached, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Routing Rule Wizard screen, click
Finish.
After creating the two new routing rules, you need to modify the
default rule. This rule redirects outbound traffic to the external ISA
Server and bypasses the Web cluster. Use the following procedure to modify
the default routing rule.
To modify the default routing rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, and then click
Network Configuration.
- In the right pane, double-click Default rule.
- In the Default rule Properties dialog box, on the
Action tab, select Routing them to a specified upstream
server, and then click Settings.
- In the Upstream Server Setting dialog box, in the Server
or array box, type 10.50.0.101, in the Port box,
ensure that 8080 is listed, in the SSL Port box,
ensure that 8443 is listed, ensure that all other check boxes are
cleared, and then click OK.
- In the Default rule Properties dialog box, click
OK.
Enabling IP Packet Filtering
Use the following procedure to verify that IP packet filtering is
enabled.
To verify that IP packet filtering is enabled
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Access
Policy, right-click IP Packet Filters, and then click
Properties.
- In the IP Packet Filters window, on the General tab,
ensure that all three check boxes are selected, and then click
OK.
Maximizing ISA Server Performance
You can maximize the performance of the ISA Server by increasing the
Performance Tuning setting. Use the following procedure to increase this
setting.
To increase the Performance Tuning setting
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, right-click <servername>, and then click
Properties.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog box, on
the Performance tab, in the Performance tuning section,
increase the setting to More than 1,000, and then click
OK.
Modifying the Hosts File
Because ISA Server is not part of a domain, you must modify the hosts
file so that ISA Server will use the www.contoso.com URL as the IP address
of the Business Desk server. By default, the hosts file is located in the
<drive>:\WINNT\system32\drivers\etc folder. You must modify
the hosts file by adding the following entry:
10.30.10.1www.contoso.com
Installing and Configuring the DMZ Web Cluster
This section provides detailed instructions for configuring the Web
servers in the perimeter network (also known as demilitarized zone or DMZ)
to support Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers (AFS).
Specifically, this section describes how to:
- Install MSXML 3.0 Service Pack 2.
- Install Internet Explorer 5.5 Service Pack 2.
- Install the .NET Framework.
- Install MDAC 2.7.
- Install MDAC 2.7 Rollup.
- Install Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5.
- Install Message Queuing (also known as MSMQ).
- Verify the Message Queuing installation.
- Disable named pipes.
- Create a new Web site for the Web servers.
- Maximize Web server performance.
- Configure the Internet connection.
- Configure proxy settings.
- Create the service account for the Web servers.
Installing MSXML 3.0 Service Pack 2
Use the following procedure on each Web server to install MSXML 3.0
Service Pack 2 (SP2).
To install MSXML 3.0 SP2
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
MSXML 3.0 SP2 installation file, and then double-click
msxml3sp2Setup.exe.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft XML Parser Setup Wizard,
click Next.
- In the End-User License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), select I accept the terms in the License
Agreement, and then click Next to proceed with installation.
- In the Customer Information screen, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
The user name. |
| Organization |
The name of your
organization. |
- Click Next.
- In the Ready to Install screen, click Install.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Completing the Microsoft XML Parser Setup Wizard,
click Finish.
Installing Internet Explorer 5.5 Service Pack 2
Use the following procedure on each Web server to install Internet
Explorer 5.5 Service Pack 2 (SP2).
To install Internet Explorer 5.5 SP2.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
Internet Explorer 5.5 SP2 setup file, and then double-click
ie5setup.exe.
- In the Welcome to Setup for Internet Explorer and Internet
Tools, read the End-User License Agreement (EULA), select I
accept the agreement, and then click Next to proceed with
installation.
- In the Windows Update: Internet Explorer and Internet Tools
screen, click Next.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Restart Computer screen, click Finish.
Installing the .NET Framework
Use the following procedure on each Web Server to install the .NET
Framework.
To install the .NET Framework
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
.NET Framework setup file, and then double-click dotnetfx.exe.
- In the Microsoft .NET Framework Setup dialog box asking if
you want to install the .NET Framework, click Yes.
- In the Microsoft .NET Framework Setup dialog box asking if
you want to update Microsoft Windows Installer components, click
Yes.
- In the Microsoft .NET Framework (English) Setup
screen, click Next.
This step starts the .NET Framework installation process.
- In the Microsoft .NET Framework (English) Setup dialog box,
click OK.
- In the System Settings Change screen, click Yes to
restart the server.
Installing MDAC 2.7
Use the following procedure on each Web server to install MDAC 2.7.
To install MDAC 2.7 on each Web server
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing MDAC
2.7 setup file, and then double-click MDAC_TYP.exe.
- In the End User License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), select I accept all of the terms of the
preceding license agreement to proceed with installation, and then
click Next.
- In the Microsoft Data Access Components 2.7 Setup screen,
click Finish.
This step starts the MDAC 2.7 installation process.
- In the Microsoft Data Access Components 2.7 Setup screen,
click Close.
Note Installing MDAC
2.7 may fail on the first attempt. Reinstall if
necessary.
Installing MDAC 2.7 Rollup
Use the following procedure on each Web server to install the MDAC 2.7
Rollup.
To install the MDAC 2.7 Rollup on each Web server
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
MDAC 2.7 Rollup setup file, and then double-click
CS_MDAC27_x86_en.exe.
- In the Microsoft Data Access Components Hotfix Installer
screen, click OK.
This step starts the MDAC 2.7 Rollup installation process.
- In the Setup is complete dialog box, click OK.
- In the System Settings Change screen, click Yes to
restart the server.
Installing Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5
Use the following procedure on each Web server to install Visual Basic
6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5 (SP5).
To install Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime SP5 on each Web server
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime SP5 setup file, and then double-click
VBRun60sp5.exe.
- In the Visual Basic 6.0 with Visual Studio 6.0 Service Pack 5 Run
Time Files dialog box, click Yes to install the Visual Basic
6.0 run time files.
This step starts the Visual Basic 6.0 Runtime Service Pack 5
installation process.
Note No dialog box will
appear to indicate that installation has completed.
Installing Message Queuing
Message Queuing (also known as MSMQ) must be installed on each Web
server as its own Message Queuing service, not as a dependent client.
To install Message Queuing
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Configure Your
Server.
- In the Windows 2000 Configure Your Server dialog box, expand
Advanced from the left column, and then select Message
Queuing.
- In the right pane, click Start the Message Queuing Installation
Wizard.
- In the Welcome to the Message Queuing Installation Wizard
screen, click Next.
The wizard may prompt you to insert the Windows 2000 CD into the
CD-ROM drive. Installation of Message Queuing starts.
- In the Completing the Message Queuing Installation Wizard
screen, click Finish.
Verifying the Message Queuing Installation
After completing the Message Queuing Installation Wizard, you must
verify that Message Queuing was installed properly and that all required
subdirectories exist.
To verify the Message Queuing installation
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the Computer Management window, expand Services and
Applications, expand Message Queuing, and then click
Private Queues.
- In the right pane, verify that the following four private queues
exist:
- admin_queue$
- mqis_queue$
- notify_queue$
- order_queue$
Disabling Named Pipes
After installation, disable named pipes and use only TCP/IP as
described in the following procedure. If your setup requires named pipes,
ensure that TCP/IP has a higher precedence than named pipes.
To disable named pipes
- Click Start, and then click Run.
- In the Run dialog box, in the Open box, type
cliconfg, and then click OK.
- In the SQL Server Client Network Utility dialog box, on the
General tab, if you have the Default network library
section, select TCP/IP from the drop-down list, and then click
OK.
–Or–
If you have a Disabled Protocols section, select
TCP/IP, and then click Enabled. If Named Pipes
appears in the Enabled protocols section, click Named
Pipes, click Disable, and then click OK.
Creating a New Web Site for the Web Servers
To avoid potential security risks associated with ISAPI and the default
Web site, you need to create a new Web site on each Web server. First, you
need to create a folder to hold the AFS Web site files, and then you need
to create the new AFS Web site.
To create a folder to contain the files for the new Web site for the
Web servers
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Accessories, and then click Windows Explorer.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the root drive.
- On the File menu, click New, and then click
Folder.
- In the right pane, in the new folder Name box, type
MySite, and then press ENTER.
Now that you have created a folder to contain the files for the new Web
site, you are ready to create the new Web site.
To create the new Web site for the Web servers
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the Computer Management window, expand Services and
Applications, expand Internet Information Services,
right-click Default Web Site, and then click Stop.
- Right-click Internet Information Services, click New,
and then click Web Site.
The Web Site Creation Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the Web Site Creation Wizard screen, click
Next.
- In the Web Site Description screen, type MySite as the
description for the new Web site, and then click Next.
- In the IP Address and Port Settings screen, accept the
default values and click Next.
- In the Web Site Home Directory screen, type the path to the
MySite folder, or click Browse to navigate to this folder.
- Select Allow anonymous access to this Web site, and then
click Next.
- In the Web Site Access Permissions screen, accept the default
values and click Next.
- In the You have successfully completed the Web Site Creation
Wizard screen, click Finish.
Maximizing Web Server Performance
You can maximize the performance of the Web servers by increasing the
Performance Tuning setting on each Web server.
To increase the Performance Tuning setting
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Services
Manager.
- In the Internet Information Services window, expand
<servername>, right-click MySite, and then
click Properties.
- In the MySite Properties dialog box, on the
Performance tab, in the Performance tuning section,
increase the setting to More than 100,000, and then click
OK.
Configuring the Internet Connection
Use the following procedure to configure the Internet connection on
each Web server.
To configure the Internet connection
- On the desktop of the Web server, double-click Connect to the
Internet.
- In the Welcome to the Internet Connection Wizard screen,
select the LAN option, and then click Next.
- In the Setting up your Internet Connection screen, select the
LAN option, and then click Next.
- In the Local Area Network Internet Configuration screen,
clear all check boxes, and then click Next.
- In the Set Up your Internet Mail Account screen, select
No, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the Internet Connection Wizard screen,
click Finish.
Configuring Proxy Settings
For the DMZ Web servers to access the Internet, you must configure the
proxy settings in Internet Explorer as described in the following
procedure on each Web server.
To configure proxy settings
- In Internet Explorer, on the Tools menu, click
Internet Options.
- In the Internet Options dialog box, on the Connections
tab, in the Local Area Network (LAN) settings section, click
LAN Settings.
- In the Local Area Network (LAN) Settings dialog box, in the
Proxy server section, select Use a proxy server, in the
Address box, type 10.10.0.100, and in the Port box,
type 8080. Select Bypass proxy server for local addresses,
and then click OK.
- In the Internet Options dialog box, click Apply, and
then click OK.
Creating the Service Account for the Web Servers
For security purposes, you will need to create a local machine account
with only User privileges on each Web server. This account will be used to
run the AFS COM+ applications.
To create the service account for the Web servers
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the Computer Management window, expand Local Users and
Groups, right-click Users, and then click New User.
- In the New User dialog box, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
AFS_Service_Account |
| Password |
The appropriate password. |
| Confirm password |
The appropriate
password. |
- Clear the User must change password at next logon box.
- Select the check boxes for User cannot change password and
Password never expires.
- Click Create, and then click Close.
Installing Commerce Server 2002
This section provides instructions for installing Commerce Server 2002
on the Business Desk server and the DMZ Web cluster. Specifically, this
section describes how to:
- Install Commerce Server 2002 on the Business Desk server.
- Install Commerce Server 2002 on the DMZ Web cluster.
Installing Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition on the
Business Desk Server
While Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition will be installed on both
the Web cluster in the DMZ and the Business Desk server in the intranet,
you must first install Commerce Server 2002 on the Business Desk server
before installing it on the Web cluster. Use the following procedure on
the Business Desk server to install Commerce Server 2002.
To install Commerce Server 2002 on the Business Desk server
- Insert the Commerce Server 2002 CD into the CD-ROM drive of the
Business Desk server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
Commerce Server 2002 setup file, and then double-click setup.exe.
The Commerce Server 2002 Setup wizard starts.
- Click Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
Components, and then follow the online prompts.
- In the Setup Type screen, select Custom, and then
click Next.
- In the Custom Setup screen, click to the left of Analysis
& Data Warehouse, and then select Entire feature will be
installed on local drive.
- Repeat step 5 for Direct Mailer Server and for Predictor
Service.
- Click Next.
- In the Administration Database Configuration screen, select
Use a specific User Name and Password, and then do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| SQL Server Computer |
The computer name of the SQL
Server. |
| SQL Server Login Name |
AFSSQL |
| SQL Server Login Password |
The corresponding
password. |
- Click Next.
- In the Microsoft Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
dialog box indicating that a new Administration database will be
created, click OK.
- In the Microsoft Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
dialog box recommending Windows Authentication, click OK.
- In the Direct Mailer Database Configuration screen, select
Use a specific User Name and Password, and then do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| SQL Server Computer |
The computer name of the SQL
Server. |
| SQL Server Login Name |
AFSSQL |
| SQL Server Login Password |
The corresponding
password. |
- Click Next.
- In the Microsoft Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
dialog box recommending Windows Authentication, click OK.
- In the Services Accounts screen, ensure that the Use the
same account for each service and set all to auto start option is
selected.
- In the Service Settings section, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Username |
AFS_Admin_Account |
| Password |
The corresponding password. |
| Domain |
Contoso |
- Click Next.
- In the Ready to Install screen, click Install.
- In the Completing the Commerce Server 2002 Setup Wizard
screen, ensure that the Register online with Microsoft option is
not selected, and then click Finish.
- In the Microsoft Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
dialog box indicating to restart server, click Yes.
Installing Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition on the
DMZ Web Cluster
For each of the three Web servers in the DMZ Web cluster, use the
following procedure to install Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise
Edition.
To install Commerce Server 2002 on the DMZ Web cluster
- Insert the Commerce Server 2002 CD into the CD-ROM drive of the Web
server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
Commerce Server 2002 setup file, and then double-click setup.exe
The Commerce Server 2002 Setup wizard starts.
- Click Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
Components, and then follow the online prompts.
- In the Setup Type screen, select Web Server, and then
click Next.
- In the Administration Database Configuration screen, select
Use a Specific User Name and Password, and then do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| SQL Server Computer |
The computer name of the SQL
Server. |
| SQL Server Login Name |
AFSSQL |
| SQL Server Login Password |
The corresponding
password. |
- Click Next.
- In the Microsoft Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
dialog box indicating that the Administration database exists, click
OK.
- In the Microsoft Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
dialog box recommending Windows Authentication, click OK.
- In the Services Accounts screen, ensure that the Use the
same account for each service and set all to auto start option is
selected.
- In the Service Settings section, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Username |
Administrator |
| Password |
The corresponding password. |
| Domain |
The server name. |
- Click Next.
- In the Ready to Install screen, click Install.
- In the Completing the Commerce Server 2002 Setup Wizard
screen, ensure that the Register online with Microsoft option is
not selected, and then click Finish.
- In the Microsoft Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
dialog box indicating to restart server, click Yes.
Installing BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Service
Release 1
This section provides instructions for installing BizTalk Accelerator
for Suppliers (AFS) Service Release 1 (SR1) on the Business Desk server,
the BizTalk Server, and the DMZ Web cluster. Specifically, this section
describes how to:
- Install AFS Service Release 1 on the Business Desk server.
- Install AFS Service Release 1 on the BizTalk Server.
- Enable HTTP catalog publishing on the BizTalk Server.
- Change the sharing permissions on the AFSCatalogPub folder.
- Install AFS Service Release 1 on the DMZ Web cluster.
- Add additional SQL permissions for the AFS_Service_Account.
- Modify the Commerce Server 2002 Microsoft Management Console.
Installing BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Service
Release 1 on the Business Desk Server
Use the following procedure on the Business Desk server to install AFS
Service Release 1 (SR1).
To install AFS SR1 on the Business Desk server
- Insert the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers CD into the
CD-ROM drive of the Business Desk server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers setup file, and then double-click
setup.exe.
The Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Setup Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers
SR1 Setup Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the License Agreement screen, read the End-User License
Agreement (EULA), select I accept the terms in the license
agreement to proceed with installation, and then click Next.
- In the Customer Information screen, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
The user name. |
| Organization |
The organization name. |
| Product key |
The product key. |
- Click Next.
- In the Platform Validation screen, verify that all
requirements for Commerce Server components are met, and then click
Next.
- In the Custom Setup screen, ensure that the Commerce
Server Components option has a server icon next to it, indicating
that it will be installed, and ensure that the BizTalk Server
Components option has an X next to it, indicating that it will not
be installed.
- Click to the left of SDK and Samples, select Entire
feature will be installed on local drive, and then click
Next.
- In the Destination Folder screen, click Change to
select a folder for installation, or click Next to use the
default installation folder.
- In the BizTalk Messaging Configuration screen, do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Username |
AFS_Service_Account |
| Password |
The corresponding password. |
| Domain |
Contoso |
- Click Next.
- In the Ready to Install the Program screen, click
Install.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Setup Wizard Completed screen, click Finish.
- In the Unpack screen, select Custom unpack, and then
click Next.
- In the Unpack Method screen, select Create a new site,
and then click Next.
- In the Site Name screen, in the Site name box, type
SupplierAccelerator, and then click Next.
- In the Select Resources screen, click Next.
- In the Global Resource Pointers screen, click Next.
- In the Database Connection Strings screen, click New
Database.
- In the New Database dialog box, select Use a specific user
name and password.
- In the New Database dialog box, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| SQL Server computer |
The computer name of SQL Server. |
| Database name |
supplieraccelerator_commerce |
| SQL user name |
AFSSQL |
| SQL password |
The corresponding
password. |
- Click Create database.
- Repeat steps 20 to 23 but use supplieraccelerator_dw for the
database name.
- In the Database Connection Strings screen, click the first
resource and while pressing the SHIFT key, click the last
resource to select all of the resources.
- In the Database Connection Strings screen, press CTRL,
and then click the Data Warehouse resource to unselect it.
- In the Database Connection Strings screen, click
Modify. This enables you to modify all the selected resource
connection strings at once.
- In the Data Link Properties dialog box, on the
Connection tab, in the Select or enter a server name box,
type the name of the SQL Server.
- In the Enter information to log on to the server section,
select Use a specific user name and password, and do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
AFSSQL |
| Password |
The corresponding
password. |
- Select Select the database on the server, select
supplieraccelerator_commerce from the drop-down list, and then
click Test Connection.
- If the connection test is successful, click OK in the
Microsoft Data Link dialog box informing you that the test
connection succeeded.
- In the Data Link Properties dialog box, click OK.
- In the Database Connection Strings screen, select the Data
Warehouse resource, and then click Modify.
- Repeat steps 28 through 32 but select supplieraccelerator_dw
from the drop-down list for the database in step 30.
- In the Database Connection Strings screen, click Next.
- In the Microsoft Commerce Server 2002 Enterprise Edition
dialog box recommending Windows Authentication, click OK.
- In the Select Applications screen, ensure that both check
boxes are selected, and then click Next.
- In the Select IIS Computers, WebSites and Paths screen,
select supplieraccelerator from the list of applications, and in
the IIS Web site section, select MySite from the drop-down
list.
- Select supplieracceleratorbizdesk from the list of
applications, and in the IIS Web site section, select MySite
from the drop-down list.
Note Ensure that both
the supplieraccelerator and supplieracceleratorbizdesk applications are
using MySite. Use the default IIS path.
- Click Next.
- In the Data Warehouse screen, click OK.
- In the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers screen, in
the BizTalk Server Name box, type the name of the BizTalk Server,
and then click OK.
- In the Profiling System screen, click Next.
- In the next Profiling System screen, click OK. It may
take several minutes for the unpacking process to complete.
- In the Unpacking is complete screen, click Finish.
- Restart the server.
Installing BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Service
Release 1 on the BizTalk Server
This section provides detailed instructions for installing AFS Service
Release 1 (SR1) on the BizTalk Server.
Use the following procedure to install AFS Service Release 1 (SR1) on
the BizTalk Server.
To install AFS SR1 on the BizTalk Server
- Insert the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers CD into the
CD-ROM drive of the BizTalk Server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers setup file, and then double-click
setup.exe.
The Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Setup Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers
SR1 Setup Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the License Agreement screen, read the End-User License
Agreement (EULA), select I accept the terms in the license
agreement to proceed with installation, and then click Next.
- In the Customer Information screen, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
The user name. |
| Organization |
The organization name. |
| Product key |
The product key. |
- Click Next.
- In the Platform Validation screen, verify that all the
requirements for BizTalk Server components are met, and then click
Next.
- In the Custom Setup screen, ensure that the BizTalk Server
Components option has a server icon next to it, indicating that it
will be installed, and ensure that the Commerce Server Components
option has an X next to it, indicating that it will not be installed,
and then click Next.
- In the Destination Folder screen, click Change to
select a folder for installation, or click Next to use the
default installation folder.
- In the BizTalk Messaging Configuration screen, do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Username |
AFS_Service_Account |
| Password |
The corresponding password. |
| Domain |
Contoso |
- Click Next.
- In the BizTalk Database Security Configuration screen, do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Username |
sa |
| Password |
The corresponding
password. |
- Click Next.
- In the Select IIS Web Site screen, ensure that Default Web
Site is selected, and then click Next.
- In the BizTalk PO Port Configuration screen, type
http://www.contoso.com/supplieraccelerator, and then click
Next.
- In the Ready to Install the Program screen, click
Install.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Setup Wizard Completed screen, click Finish.
Enabling HTTP Catalog Publishing
To enable HTTP catalog publishing, you must add proxy server settings
to the BizTalk Server Administration.
To add proxy server settings to the BizTalk Server
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
BizTalk Server 2002, and then click BizTalk Server
Administration.
- In the BizTalk Server Administration window, expand
Microsoft BizTalk Server 2002, right-click BizTalk Server
Group, and then click Properties.
- In the BizTalk Server Group Properties dialog box, on the
General tab, in the Proxy server section, select Use a
proxy server.
- In the Address box, type the Private IP address of the
intranet ISA Server. The example IP address used in this document is
10.30.0.100.
- In the Port box, type 8080, and then click OK.
Changing the Sharing Permissions on the AFSCatalogPub
Folder
Use the following procedure to grant full control for only the
AFS_Service_Account domain account and the local BizTalk Server
Administrators group on the AFSCatalogPub folder.
To change the sharing permissions on the AFSCatalogPub folder
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the
<drive>:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application
Data folder, right-click the AFSCatalogPub folder, and then
click Properties.
- In the AFSCatalogPub Properties dialog box, on the
Security tab, in the Name section, select Everyone,
and ensure that the option Allow inheritable permissions from parent
to propagate to this object is not selected.
- In the Security dialog box, click Remove.
- In the Name section, select AFS_Service_Account, in
the Permissions section, select Allow Full Control, and
then click Add.
- In the Select Users, Computers, or Groups box, type
<servername>\BizTalk Server Administrators, and then
click OK.
- In the Name section, select BizTalk Server
Administrators, and in the Permissions section, select
Allow Full Control.
- Click OK.
Installing AFS Service Release 1 on the DMZ Web
Cluster
Use the following procedure on each server in the Web cluster to
install AFS Service Release 1 (SR1).
To install AFS SR1 on the Web cluster servers
- Insert the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers CD into the
CD-ROM drive of the Web server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers setup file, and then double-click
setup.exe.
The Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Setup Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers
SR1 Setup Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the License Agreement screen, read the End-User License
Agreement (EULA), select I accept the terms in the license
agreement to proceed with installation, and then click Next.
- In the Customer Information screen, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
The user name. |
| Organization |
The organization name. |
| Product key |
The product key. |
- Click Next.
- In the Platform Validation screen, verify that all
requirements for Commerce Server components are met, and then click
Next.
- In the Custom Setup screen, ensure that the Commerce
Server Components option has a server icon next to it, indicating
that it will be installed, and ensure that the BizTalk Server
Components option has an X next to it, indicating that it will not
be installed, and then click Next.
- In the Destination Folder screen, click Change to
select a folder for installation, or click Next to use the
default installation folder.
- In the BizTalk Messaging Configuration screen, do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Username |
AFS_Service_Account |
| Password |
The corresponding password. |
| Domain |
The name of the
server. |
- Click Next.
- In the Ready to Install the Program screen, click
Install.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Setup Wizard Completed screen, click Finish.
- In the Unpack screen, select Custom unpack, and then
click Next.
- In the Unpack Method screen, select Add a Web server to an
existing application in an existing site, and then click
Next.
- In the Select Site screen, in the Existing sites
section, select SupplierAccelerator, and then click Next.
- In the Select Applications screen, clear the check box for
supplieracceleratorbizdesk, and then click Next.
- In the Select IIS Computers, Web Sites and Paths screen,
ensure that the supplieraccelerator application is displayed.
- In the IIS Web site section, ensure that MySite is
selected from the drop-down list, and then click Next.
- In the Unpacking is complete screen, click Finish.
- Restart the server.
Adding Additional SQL Permissions for the
AFS_Service_Account
Use the following procedure to grant permissions on the BizTalk
databases for the user AFS_Service_Account.
To grant permissions on the BizTalk databases for the
AFS_Service_Account
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
SQL Server, and then click Enterprise Manager.
- In SQL Server Enterprise Manager, expand Microsoft SQL
Servers, expand SQL Server Group, expand
<servername>, expand Security, and then click
Logins.
- In the right pane of Enterprise Manager in the list of users,
right-click contoso\AFS_Service_Account user, and then click
Properties.
- In the SQL Server login Properties –
contoso\AFS_Service_Account dialog box, on the Database
Access tab, in the Specify which databases can be accessed by the
login box, select the check box for InterchangeSQ.
- In the Database roles for InterchangeSQ box, select
db_owner.
- In the Specify which databases can be accessed by the login
box, select the check box for InterchangeDTA.
- In the Database roles for InterchangeDTA box, select
db_owner.
- In the SQL Server login Properties –
contoso\AFS_Service_Account dialog box, click OK.
Modifying the Commerce Server 2002 MMC
To access the site properly, you need to modify the Commerce Server
2002 Microsoft Management Console (MMC) settings so that the proper Web
site name is used. This only needs to be modified on one of the Web
servers (or on the Business Desk server).
To modify the Commerce Server 2002 MMC
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
Commerce Server 2002, and then click Commerce Server Manager.
- In the Commerce Server 2002 window, expand Commerce Server
Manager, expand Commerce Sites, expand
SupplierAccelerator, and then expand Applications.
- Right-click <servername>/supplieraccelerator,
and then click Properties.
- In the <servername>/supplieraccelerator
Properties dialog box, in the Nonsecure host name box,
type www.contoso.com, and then click OK.
- Right-click
<servername>/supplieracceleratorbizdesk, and then
click Properties.
- In the <servername>/supplieracceleratorbizdesk
Properties dialog box, in the Nonsecure host name box,
type www.contoso.com, and then click OK.
- Click Start, and then click Run.
- In the Run dialog box, in the Open box, type
iisreset, and then click OK.
- Repeat steps 7 and 8 on all the Web servers and the Business Desk
server
Installing and Configuring the External ISA Server
This section provides detailed instructions for installing and
configuring the external ISA Server. Specifically, this section describes
how to:
- Remove Internet Information Services (IIS).
- Install ISA Server Standard Edition.
- Install ISA Server Service Pack 1.
- Install Windows 2000 Hotfix Q315764.
- Modify ISA Server properties.
- Add incoming Web request listeners.
- Create a new site and content rule.
- Create new protocol rules.
- Create destination sets.
- Create Web publishing rules.
- Create new routing rules.
- Enable IP packet filtering.
- Modify the hosts file.
- Maximize ISA Server performance.
Removing Internet Information Services
If you installed Internet Information Services (IIS) by default on the
external ISA Server when you installed Windows 2000, you can remove it
because it is not needed.
To remove IIS from the external ISA Server
- Click Start, point to Settings, and then click
Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, double-click Add/Remove Programs.
- In Add/Remove Programs, click Add/Remove Windows
Components from the left column.
The Windows Components Wizard starts.
- In the Windows Components screen, clear the check box for
Internet Information Services (IIS), and then click Next.
You might have to scroll down to view the Internet Information
Services (IIS) component.
- If the Terminal Services Setup screen appears, select
Remote administration mode, and then click Next. The
wizard might take a few minutes to complete.
- In the Completing the Windows Components Wizard screen, click
Finish.
IIS is now uninstalled.
- Click Close to exit Add/Remove Programs.
Installing ISA Server Standard Edition
After you have removed IIS, you can install ISA Server.
To install ISA Server Standard Edition
- Insert the ISA Server 2000 Standard Edition CD into the CD-ROM drive
of the external ISA Server.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
ISA Server 2000 setup file, and then double-click ISAAutorun.exe.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server Setup screen, select Install
ISA Server.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server (Standard Edition) Setup dialog
box, click Continue.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server Setup dialog box, read the
End-User License Agreement (EULA), and then click I Agree to
accept the terms of the EULA to proceed with installation.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server (Standard Edition) Setup dialog
box, click Full Installation.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server Setup dialog box, select
Integrated mode, and then click Continue.
- In the Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server
Setup dialog box, click OK to accept the default location and
size for the ISA Server cache drives.
- In the Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server
Setup dialog box for entering the IP address ranges, click
Construct Table.
- In the Local Address Table dialog box, clear the check box
for Add the following private ranges, select Add address
ranges based on the Windows 2000 Routing Table, select the
Private and Dedicated network adapters, and then click
OK. The example IP addresses in this document are 10.10.0.100 and
10.50.0.101, respectively.
- In the Setup Message dialog box, click OK.
- In the Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server
Setup dialog box for entering the IP address ranges, click
OK.
- If a message box appears, informing you that Message Screener
requires the SMTP Service, click OK.
The ISA Server installation starts.
- In the Launch ISA Management Tool dialog box, clear the check
box for starting up the wizard, and then click OK.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server (Standard Edition) Setup dialog
box that states that ISA Server Setup was completed successfully, click
OK.
Installing ISA Server Service Pack 1
After you install ISA Server, you can install ISA Server Service Pack 1
(SP1).
To install ISA Server SP1
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
ISA Server SP1 setup file, and then double-click ISASP1.exe.
- In the Software License Agreement screen, read the End-User
License Agreement (EULA), and select I agree to proceed with
installation.
Installation starts.
- In the Microsoft ISA Server 2000 Update Setup dialog box,
click OK.
- The server will restart after the Service Pack is installed.
Installing Windows 2000 Hotfix Q315764
Use the following procedure to install Windows 2000 Hotfix Q315764.
To install Windows 2000 Hotfix Q315764
- In Internet Explorer, navigate to http://support.microsoft.com/.
Search for the KB Article Q321828 and follow the online installation
instructions.
Modifying ISA Server Properties
After installing ISA Server, modify its properties so that requests
containing sensitive data (requests for confirm.asp and crdtcard.asp) can
be forwarded to the intranet ISA Server. Because the processing of these
pages consumes more resources, the forwarding performed by the external
ISA Server provides load balancing (between the DMZ Web cluster and
intranet Business Desk server) and relieves the DMZ Web cluster of
processing these requests. With this forwarding, the DMZ Web cluster can
achieve better performance in serving Web sites.
Adding Incoming Web Request Listeners
Because ISA Server intercepts requests from external clients for
internal servers, you must specify which IP addresses will listen for Web
requests from external clients. Use the following procedure to add
incoming Web request listeners.
To add incoming Web request listeners
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, right-click <servername>, and
then click Properties.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog box, on
the Incoming Web Requests tab, select Configure listeners
individually per IP address, and then click Add.
- In the Add/Edit Listeners dialog box, click the drop-down
list for Server and select
<servername>.
- Click the drop-down list for IP Address, and select the IP
address corresponding to the Public network adapter.
- Clear all check boxes except for Integrated, and then click
OK.
- In the <servername> Properties
dialog box, click Apply.
- In the ISA Server Warning dialog box, select Save the
changes and restart the service(s), and then click OK.
- In the <servername> Properties
dialog box, click OK.
Creating a New Site and Content Rule
Site and content rules determine if and when content on specific
destination sets can be accessed by specified users. Use the following
procedure to create a new site and content rule.
To create a new site and content rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In ISA Management, expand Servers and Arrays, expand
<servername>, expand Access Policy, right-click Site
and Content Rules, click New, and then click Rule.
This step starts the New Site and Content Rule Wizard.
- In the Welcome to the New Site and Content Rule Wizard
screen, in the Site and content rule name box, type Allow,
and then click Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, ensure that Allow is
selected, and then click Next.
- In the Rule Configuration screen, ensure that Allow access
based on destination is selected, and then click Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, ensure that All
destinations is selected from the drop-down list, and then click
Next.
- In the Completing the New Site and Content Rule Wizard
screen, click Finish.
Creating New Protocol Rules
Protocol rules determine which protocols clients can use and when. Use
the following procedure to create the Outgoing Web Traffic protocol
rule.
To create the Outgoing Web Traffic protocol rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In ISA Management, expand Servers and Arrays, expand
<servername>, expand Access Policy, right-click
Protocol Rules, click New, and then click Rule.
The New Protocol Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Protocol Rule Wizard screen, in the
Protocol rule name box, type Outgoing Web Traffic, and
then click Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, ensure that Allow is
selected, and then click Next.
- In the Protocols screen, ensure that Selected
protocols is selected from the drop-down list. In the
Protocols section, ensure that the HTTP, HTTPS, and
Show only selected protocols options are selected, and then click
Next.
- In the Schedule screen, ensure that Always is selected
from the drop-down list, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, ensure that Any request is
selected, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Protocol Rule Wizard screen, click
Finish.
Creating Destination Sets
A destination set is defined as a set of path locations or a specific
IP range. Destination sets are used by routing or publishing rules to
define a specific set of destinations. Use the following procedure to
create the SupplierAccelerator, Confirm, and Forbidden destination
sets.
The SupplierAccelerator destination set defines all the ASP pages in
the supplieraccelerator site.
To create the SupplierAccelerator destination set
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Policy
Elements, right-click Destination Sets, click New, and
then click Set.
- In the New Destination Set dialog box, in the Name
box, type SupplierAccelerator, and then click Add.
- In the Add/Edit Destination dialog box, select
Destination, and then type an asterisk (*).
- In the Path box, type /supplieraccelerator/*, and then
click OK.
- In the New Destination Set dialog box, click OK.
The Confirm destination set defines the two ASP pages that are used by
purchase order processing.
To create the Confirm destination set
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Policy
Elements, right-click Destination Sets, click New, and
then click Set.
- In the New Destination Set dialog box, in the Name
box, type Confirm, and then click Add.
- In the Add/Edit Destination dialog box, select
Destination, and then type www.contoso.com.
- In the Path box, type
/supplieraccelerator/confirm.asp, and then click OK.
- In the New Destination Set dialog box, click Add.
- In the Add/Edit Destination dialog box, select
Destination, and then type www.contoso.com.
- In the Path box, type
/supplieraccelerator/crdtcard.asp, and then click OK.
- In the New Destination Set dialog box, click OK.
The Forbidden destination set defines ASP pages that Internet clients
are forbidden to access.
To create the Forbidden destination set
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Policy
Elements, right-click Destination Sets, click New, and
then click Set.
- In the New Destination Set dialog box, in the Name
box, type Forbidden, and then click Add.
- In the Add/Edit Destination dialog box, select
Destination, and then type www.contoso.com.
- In the Path box, type
/supplieraccelerator/BDRefresh.asp, and then click OK.
- In the New Destination Set dialog box, click OK.
Creating Web Publishing Rules
You need to create three Web publishing rules named NLB IIS Web
Servers, Confirm, and Forbidden to define how incoming Web requests will
be handled.
Note It is important that
the rules be listed in the following order: Forbidden, Confirm, NLB IIS
Web Servers, and Default. The order of the rules can be set by using the
UP or DOWN arrow in the ISA Management window.
The NLB IIS Web Server rule directs all Web traffic to the DMZ Web
servers. Use the following procedure to create the NLB IIS Web Servers Web
publishing rule.
To create the NLB IIS Web Servers Web publishing rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In ISA Management, expand Servers and Arrays, expand
<servername>, expand Publishing, right-click Web
Publishing Rules, click New, and then click Rule.
The New Web Publishing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
in the Web publishing rule name box, type NLB IIS Web
Servers, and then click Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, ensure that Specified
destination set is selected from the drop-down list.
- In the Name drop-down list, ensure that
SupplierAccelerator is selected, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, select Any Request, and
then click Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, select Redirect the request
to this internal Web server (name or IP address), and then type
the name of the Web cluster in the text box next to the Browse
button. The example name used in this document is
www.contoso.com.
- Select Send the original host header to the publishing
server, use the default ports, and then click Next.
All requests will be redirected to the Web cluster.
- In the Completing the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
click Finish.
- In the ISA Management window, double-click the NLB IIS Web
Servers rule.
- In the NLB IIS Web Servers Properties dialog box, on the
Bridging tab, in the Redirect SSL requests as section,
ensure that HTTP requests is selected, and then click OK.
The confirm rule redirects any purchase order request (for the
confirm.asp or crdtcard.asp pages) to the Business Desk server instead of
to the Web servers. Use the following procedure to create the Confirm Web
publishing rule.
To create the Confirm Web publishing rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand
Publishing, right-click Web Publishing Rules, click
New, and then click Rule.
The New Web Publishing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
in the Web publishing rule name box, type Confirm, and
then click Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, ensure that Specified
destination set is selected from the drop-down list.
- In the Name drop-down list, ensure that Confirm is
selected, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, ensure that Any Request is
selected, and then click Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, select Redirect the request
to this internal Web server (name or IP address), and then type
the IP address corresponding to the Dedicated network adapter of
the intranet ISA Server in the text box next to the Browse
button. The example IP address used in this document is
10.50.0.100.
- Select Send the original host header to the publishing
server, use the default ports, and then click Next.
All requests will be redirected to the intranet ISA Server.
- In the Completing the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
click Finish.
- In the ISA Management window, double-click the Confirm
rule.
- In the Confirm Properties dialog box, on the Bridging
tab, in the Redirect SSL requests as section, ensure that HTTP
requests is selected, and then click OK.
The Forbidden rule denies all access from external clients. Use the
following procedure to create the Forbidden Web publishing rule.
To create the Forbidden Web publishing rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand
Publishing, right-click Web Publishing Rules, click
New, and then click Rule.
The New Web Publishing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
in the Web publishing rule name box, type Forbidden, and
then click Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, ensure that Specified
destination set is selected from the drop-down list.
- In the Name drop-down list, ensure that Forbidden is
selected, and then click Next.
- In the Client Type screen, ensure that Any Request is
selected, and then click Next.
- In the Rule Action screen, ensure that Discard the Request
is selected, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Web Publishing Rule Wizard screen,
click Finish.
- In the ISA Management window, double-click the
Forbidden rule.
- In the Confirm Properties dialog box, on the Bridging
tab, in the Redirect SSL requests as section, ensure that HTTP
requests is selected, and then click OK.
Creating New Routing Rules
Routing rules determine whether a client's Web request is retrieved
directly, routed to an upstream ISA Server, or routed to an alternative
destination. Use the following procedure to create the contoso.com routing
rule.
To create the contoso.com routing rule
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In ISA Management, expand Servers and Arrays, expand
<servername>, expand Network Configuration,
right-click Routing, click New, and then click Rule.
The New Routing Rule Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the New Routing Rule Wizard screen, in the
Routing rule name box, type contoso.com, and then click
Next.
- In the Destination Sets screen, ensure that All internal
destinations is selected from the drop-down list, and then click
Next.
- In the Request Action screen, ensure that Retrieve them
directly from specified destination is selected, and then click
Next.
- In the Cache Retrieval Configuration screen, ensure that A
valid version of the object is selected, and then click Next.
- In the Cache Content Configuration screen, ensure that If
source and request headers indicate to cache, then the content will be
cached is selected, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the New Routing Rule Wizard screen, click
Finish.
Enabling IP Packet Filtering
Use the following procedure to verify that IP packet filtering is
enabled.
To verify that IP packet filtering is enabled
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, expand <servername>, expand Access
Policy, right-click IP Packet Filters, and then click
Properties.
- In the IP Packet Filters window, on the General tab,
ensure that all three check boxes are selected, and then click
OK.
Modifying the Hosts File
You must modify the hosts file so that ISA Server will use the URL
www.contoso.com as the virtual IP (VIP) address of the DMZ Web servers. By
default, the hosts file is located in the
<drive>:\WINNT\system32\drivers\etc folder. Add the following
entry to the hosts file:
10.10.0.10www.contoso.com
Maximizing ISA Server Performance
You can maximize the performance of the ISA Server by increasing the
Performance Tuning setting. Use the following procedure to increase this
setting.
To increase the Performance Tuning setting
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, right-click <servername>, and then click
Properties.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog
box, on the Performance tab, in the Performance tuning
section, increase the setting to More than 1,000, and then click
OK.
Configuring Secure Sockets Layer on the Web Site
You will need to obtain a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate and
install it on the external ISA Server. After installing your SSL
certificate, you will need to configure your external ISA Server and
configure Commerce Server Manager.
Use the following procedures to configure the external ISA Server and
Commerce Server Manager for SSL.
To configure the external ISA Server for SSL
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft
ISA Server, and then click ISA Management.
- In the ISA Management window, expand Servers and
Arrays, right-click <servername>, and then click
Properties.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog box, on
the Incoming Web Requests tab, select the Enable SSL
listeners check box.
- In the SSL Listeners dialog box, click OK.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog box,
select the public IP from the list box, and then click Edit.
- In the Add/Edit Listeners dialog box, select Use a server
certificate to authenticate to web clients, and then click
Select.
- In the Select Certificate dialog box, select the SSL
certificate, and then click OK.
- In the Add/Edit Listeners dialog box, click OK.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog box, click
Apply.
- In the ISA Server Warning dialog box, select Save the
Changes and Restart the service(s), and then click OK.
- In the <servername> Properties dialog box, click
OK.
To configure Commerce Server Manager for SSL
- On the Business Desk server, click Start, point to
Programs, point to Microsoft Commerce Server 2002, and
then click Commerce Server Manager.
- In the Commerce Server 2002 window, expand Commerce Server
Manager, expand Commerce Sites, expand
SupplierAccelerator, and then expand Applications.
- Right-click www.contoso.com/supplieraccelerator, and
then click Properties.
- In the www.contoso.com/supplieraccelerator
Properties dialog box, select Enable HTTPS.
- In the Secure host name box, type www.contoso.com, and
then click OK.
- Click Start, and then click Run.
- In the Run dialog box, in the Open box, type
iisreset, and then click OK.
- Repeat steps 6 and 7 on all the Web servers.
Locking Down the System
The following section describes additional configuration details that
can help you to secure the system.
IIS Lockdown Tool
IIS Lockdown is a tool released by Microsoft that can help system
administrators to close unused ports, services, and file extensions. This
tool can be obtained from the Microsoft Security Toolkit or from the
following URL:
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/tools/locktool.asp
You will need to run the IIS Lockdown tool on the BizTalk Server, the
Business Desk server, and the Web servers. You will need to copy the
correct urlscan.ini file from the SDK folder in the Business Desk server
to each server that will be locked down. Copy the .ini files onto a floppy
disk.
To copy the urlscan.ini files to a floppy disk from the Business
Desk server
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the
<drive>:\Program Files\Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for
Suppliers\urlscan folder and copy urlscan_afs_biztalk.ini and
urlscan_afs_commerce.ini to the floppy disk.
Use the following procedures to run the IIS Lockdown tool on the
appropriate servers.
To run the IIS Lockdown tool on the BizTalk Server
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
IIS Lockdown tool setup file, and then double-click iislockd.exe.
- In the Welcome to the Internet Information Services Lockdown
Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the End-User License Agreement screen, read the license
agreement, click I agree, and then click Next.
- In the Select Server Template screen, select BizTalk
Server 2000, select View template settings, and then click
Next.
- In the Internet Services screen, ensure that Web service
(HTTP) and Remove unselected services are the only check
boxes selected, and then click Next.
- In the Internet Information Services Lockdown Wizard dialog
box confirming the removal of services, click Yes.
- In the Script Maps screen, disable all selected script maps
except for Active Server Pages (have only the ASP check box
cleared), and then click Next.
- In the Additional Security screen, select all check boxes
except Disable Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV),
and then click Next.
- In the URLScan screen, select Install URLSCAN, and
then click Next.
- In the Ready to Apply Settings screen, click Next.
- In the Applying Security Settings screen, click Next.
- In the Completing the Internet Information Services Lockdown
Wizard screen, click Finish.
- In Windows Explorer, delete the urlscan.ini file from the
<drive>:\WINNT\system32\inetsrv\urlscan folder.
- Rename the urlscan_afs_biztalk.ini file to urlscan.ini and copy it
to the <drive>:\WINNT\system32\inetsrv\urlscan folder.
- Restart the server.
To run the IIS Lockdown tool on the Business Desk server and the Web
servers
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
IIS Lockdown tool setup file, and then double-click iislockd.exe.
- In the Welcome to the Internet Information Services Lockdown
Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the End-User License Agreement screen, read the license
agreement, click I agree, and then click Next.
- In the Select Server Template screen, select Commerce
Server 2000, select View template settings, and then click
Next.
- In the Internet Services screen, ensure that Web service
(HTTP) and Remove unselected services are the only check
boxes selected, and then click Next.
- In the Internet Information Services Lockdown Wizard dialog
box confirming the removal of services, click Yes.
- In the Script Maps screen, disable all selected script maps
except for Active Server Pages (have only the ASP check box
cleared), and then click Next.
- In the Additional Security screen, select all check boxes,
and then click Next.
- In the URLScan screen, select Install URLSCAN, and
then click Next.
- In the Ready to Apply Settings screen, click Next.
- In the Applying Security Settings screen, click Next.
- In the Completing the Internet Information Services Lockdown
Wizard screen, click Finish.
- In Windows Explorer, delete the urlscan.ini file from the
<drive>:\WINNT\system32\inetsrv\urlscan folder.
- Rename the urlscan_afs_commerce.ini file to urlscan.ini and copy it
to the <drive>:\WINNT\system32\inetsrv\urlscan folder.
- Restart the server.
Verifying Installation
This section provides instructions about verifying proper functionality
of the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers (AFS) deployment.
Specifically, this section contains information about verifying catalog
publishing and order reception functionality.
To verify proper functionality of the deployment, install the Business
Desk client on a client workstation. You cannot verify proper
functionality by using the Business Desk server directly. The client
workstation containing the Business Desk client should have Internet
Explorer (IE) 5.5 Service Pack 2 and OWC10 installed. Use the following
procedure to install the Business Desk client on a client workstation.
Installing the Business Desk Client
To install the Business Desk client, complete the following tasks:
- Establish network connectivity.
- Join the intranet domain.
- Add the AFS_Admin_Account user to the Administrators group.
- Install the AFS Software Development Kit (SDK).
- Configure the Internet connection.
- Configure proxy settings.
- Configure the Business Desk client.
Establishing Network Connectivity
Use the following procedure to establish network connectivity on the
Business Desk client workstation.
To establish network connectivity on the Business Desk client
workstation
- On the desktop, right-click My Network Places, and then click
Properties.
- In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click
Local Area Connection, and then click Properties.
- In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, click
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box,
select Use the following IP address, and do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| IP address |
10.30.30.1 |
| Subnet mask |
255.255.0.0 |
| Default gateway |
10.30.0.100 |
- Select Use the following DNS server addresses, and do the
following:
| Field |
Enter |
| Preferred DNS server |
10.30.0.200 |
- Click Advanced.
- In the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box, on the DNS
tab, select Append these DNS suffixes (in order), and then click
Add.
- In the TCP/IP Domain Suffix dialog box, type
contoso.com, and then click Add.
- In the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box, click OK.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box,
click OK.
- In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, click
OK.
Joining the Intranet Domain
Use the following procedure to join the Business Desk client computer
to the intranet domain.
To join the Business Desk client computer to the intranet domain
- On the desktop, right-click My Computer, and then click
Properties.
- In the System Properties dialog box, on the Network
Identification tab, click Properties.
- In the Identification Changes dialog box, in the Member
of section, select Domain, type contoso.com, and then
click OK.
- In the Domain Username and Password dialog box, type
administrator, type the password, and then click OK.
- In the Network Identification dialog box that welcomes you to
the domain, click OK.
- In the Network Identification dialog box that advises you to
restart the computer, click OK.
- In the System Properties dialog box, click OK.
- In the System Settings Change dialog box, click Yes to
restart the computer.
Adding the AFS_Admin_Account User to the Administrators
Group
Use the following procedure to add the AFS_Admin_Account user to the
Administrators group.
To add the AFS_Admin_Account user to the Administrators group
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the Computer Management window, expand Local Users and
Groups, and then click Groups.
- In the right pane, double-click Administrators.
- In the Administrators Properties dialog box, click
Add.
- In the Select Users or Groups dialog box, in the Look
in box, select Contoso.com from the drop-down list.
- Click the AFS_Admin_Account account, click Add, and
then click OK to close the dialog box.
- In the Administrators Properties dialog box, click
Apply, and then click Add to apply the settings and close
the dialog box.
- Close the Computer Management window.
- Log off, and then log back on to the Contoso.com domain as
AFS_Admin_Account.
Installing the AFS SDK
Use the following procedure to install the BizTalk Accelerator for
Suppliers Software Development Kit (SDK). You will need the SDK to verify
proper functionality of the deployment.
To install the AFS SDK
- Insert the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers CD into the
CD-ROM drive.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the
BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers setup file, and then double-click
setup.exe.
The Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers Setup Wizard starts.
- In the Welcome to the Microsoft BizTalk Accelerator for Suppliers
SR1 Setup Wizard screen, click Next.
- In the License Agreement screen, read the End-User License
Agreement (EULA), select I accept the terms in the license
agreement to proceed with installation, and then click Next.
- In the Customer Information screen, do the following:
| Field |
Enter |
| User name |
The user name. |
| Organization |
The organization name. |
| Product key |
The product key. |
- Click Next.
- In the Platform Validation screen, click Next.
- In the Custom Setup screen, ensure that the BizTalk Server
Components and Commerce Server Components options have an X
next to them, indicating that they will not be installed. Make sure that
SDK and Samples and Online Documentation options have a
server icon next to them, indicating that they will be installed, and
then click Next.
- In the Destination Folder screen, click Change to
select a folder for installation, or click Next to use the
default installation folder.
- In the Ready to Install the Program screen, click
Install.
This step starts the installation process.
- In the Setup Wizard Completed screen, click Finish.
Configuring the Internet Connection
Use the following procedure to configure the Internet connection.
To configure the Internet connection
- On the desktop, double-click Connect to the Internet.
- In the Welcome to the Internet Connection Wizard screen,
select LAN, and then click Next.
- In the Setting up your Internet Connection screen, select
LAN, and then click Next.
- In the Local Area Network Internet Configuration screen,
clear all check boxes, and then click Next.
- In the Set Up your Internet Mail Account screen, select
No, and then click Next.
- In the Completing the Internet Connection Wizard screen,
click Finish.
Configuring Proxy Settings
For the Business Desk client to access the Internet, you must configure
the proxy settings in Internet Explorer as described in the following
procedure.
To configure proxy settings
- In Internet Explorer, on the Tools menu, click
Internet Options.
- In the Internet Options dialog box, on the Connections
tab, in the Local Area Network (LAN) settings section, click
LAN Settings.
- In the Local Area Network (LAN) Settings dialog box, in the
Proxy server section, select Use a proxy server, in the
Address box, type 10.30.0.100, and in the Port box,
type 8080. Do not select Bypass proxy server for local
addresses, and then click OK.
- In the Internet Options dialog box, click Apply, and
then click OK.
Configuring the Business Desk Client
Use the following procedure to configure the Business Desk client.
To configure the Business Desk client
- In Internet Explorer, in the Address box, type
http://<Business Desk server
name>/supplieracceleratorbizdesk, and then press ENTER.
Note You must use the
explicit Business Desk server name. You cannot use the domain name or
the IP address of the Business Desk server.
- If the security settings of the browser prevent the site from
opening, ensure that you have enabled the following security settings in
Internet Options:
- Download signed ActiveX® controls
- Download unsigned ActiveX controls
- Initialize and script ActiveX controls not marked as safe
- Follow the instructions on the remaining screens to start Business
Desk.
Verifying Functionality
To confirm the successful installation of AFS, it is recommended that
you verify the order reception and catalog publishing functionality by
using sample data provided in the AFS SDK. For detailed information about
verifying a successful installation, see "Confirming Successful
Installation" in the AFS Help.
Completing the Deployment
Before you connect your solution to the public Internet, complete the
following steps to ensure the safety of the network:
- Apply the prescribed service packs for all software on all servers.
- Apply the IIS Lockdown tool and any known hotfixes from http://www.microsoft.com/security.
- On the ISA Servers, do not publish the entire site or IP address.
Always use a specific destination to publish a site. For example, use
www.contoso.com/supplieraccelerator instead of www.contoso.com. Create
the destination sets before publishing any site.
- Disable all unnecessary services that might potentially expose
security holes that can be exploited by malicious users. Consider
disabling the following services:
- Terminal Services
- SMTP
- Remote registry service
- Run as service
- RRAS
- NNTP
- Messenger
- IIS Admin service
- Front Page extensions
- Sample sites
- FTP
- Administration site
Known Issues
You might encounter the following issues while performing the
deployment:
- For high availability, the external ISA Server can be configured in
an array. For more information, see http://www.microsoft.com/technet/treeview/default.asp?url=/TechNet/prodtechnol/isa/proddocs/isadocs/CMT_ServerComp.asp.
- If the date settings on the Business Desk server and the DMZ Web
servers become unsynchronized, site users might inadvertently be
redirected to the default.asp page. This occurs because the Web servers
mistakenly expire the user's session.
- Network Load Balancing can only detect network failures and not HTTP
failures. If your Web service is down, Network Load Balancing will not
detect it. To detect HTTP failures, use the HTTPMon tool, which is
available in the Microsoft Windows 2000 Resource Kit.
- You should always reboot your servers after installing or
uninstalling AFS.
- For medium deployments, you must edit the global_cache_lib.asp file
in the supplieraccelerator/include folder by adding the line:
oCacheManager.RefreshCache("advertising")
after the following line:
Set oCacheManager.WriterConfig("advertising") = dictCampaignConfig
- For medium deployments, you must edit the global_cache_lib.asp file
in the supplieraccelerator/include folder by adding the line:
oCacheManager.RefreshCache("discounts")
after the following line:
Set oCacheManager.WriterConfig("discounts") = dictCampaignConfig
- If messages are stuck in the Retry queue, you must move them to the
Suspended queue and then resubmit them.
- To prevent the loss of purchase orders in a failure scenario, you
must either cluster the SQL Servers or wrap the XLANG functions in a
transaction.
- If the network connection to a Business Desk server was
disconnected, you must run IISReset at the command prompt. Until
you run IISReset, any orders that are directed to this server are
sent back to the BizTalk Server Retry queue. The following error
messages are displayed:
| Event type |
Error |
| Event Source |
SupplierAccelerator |
| Event Category |
Purchase Order |
| Event ID |
200 |
| Date |
<as appropriate> |
| Time |
<as appropriate> |
| User |
N/A |
| Computer |
<as appropriate> |
| Description |
_recvpo.asp Microsoft Commerce OLE DB
Provider: HRESULT: -2147217915, Minor Code: 0, Source: Microsoft
OLE DB Provider for SQL Server, Description Object was
open. |
| Event type |
Error |
| Event Source |
Commerce Server 2002 |
| Event Category |
None |
| Event ID |
32769 |
| Date |
<as appropriate> |
| Time |
<as appropriate> |
| User |
N/A |
| Computer |
<as appropriate> |
| Description |
In BindArgs::OpenDataSrc(), failed
initializing data source (-904429548) |
| Event type |
Error |
| Event Source |
Commerce Server 2002 |
| Event Category |
None |
| Event ID |
32773 |
| Date |
<as appropriate> |
| Time |
<as appropriate> |
| User |
N/A |
| Computer |
<as appropriate> |
| Description |
DataSource::Init(DS-1217-Profile
Definitions) failed on catalog load
(-904429548) |
| Event type |
Error |
| Event Source |
Commerce Server 2002 |
| Event Category |
None |
| Event ID |
32788 |
| Date |
<as appropriate> |
| Time |
<as appropriate> |
| User |
N/A |
| Computer |
<as appropriate> |
| Description |
Catalog Load failed catalog: Profile
Definitions (-2147217915) |
| Event type |
Error |
| Event Source |
Commerce Server 2002 |
| Event Category |
None |
| Event ID |
32 |
| Date |
<as appropriate> |
| Time |
<as appropriate> |
| User |
N/A |
| Computer |
<as appropriate> |
| Description |
'Select' statement failed for
Catalog.Catalog name: Profile Definitions, Table name:
CommerceServerCatalogs, SCODE: -2147217915 |
| Event type |
Error |
| Event Source |
Commerce Server 2002 |
| Event Category |
None |
| Event ID |
32792 |
| Date |
<as appropriate> |
| Time |
<as appropriate> |
| User |
N/A |
| Computer |
<as appropriate> |
| Description |
HRESULT: -2147217915, Minor Code: 0,
Source: Microsoft OLE DB Provider for SQL Server, Description
Object was open. |
- When publishing a catalog that has over 60,000 SKUs, you will need
to change the Server.ScriptTimeout value from 2000 to a higher number
(preferably to 8000) in the publish.asp file located in the
supplieraccelerator folder.
- To prevent potential time-outs on your site, extend the ASP time-out
period to 10 minutes.
To extend the ASP time-out period to 10 minutes
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to
Microsoft Commerce Server 2002, and then click Commerce
Server Manager.
- In the Commerce Server Manager window, expand Internet
Information Services, expand <servername>,
right-click the site you unpacked, and then click Properties.
- In the Properties dialog box, on the Home Directory
tab, under Application Settings, click Configuration.
- In the Application Configuration dialog box, on the App
Options tab, type 600 for the ASP Script timeout period.
- Click OK twice to save the setting.
- You should increase the time-outs in two of the ASP pages for large
purchase order items (100 or more line items) to be submitted properly.
The two pages are afs_PO_Const.asp, located in the
supplieraccelerator\include folder, and ReceivePO.asp, located in the
supplieraccelerator folder.
- For the afs_PO_Const.asp page, change the value of the following
line from 20 to 300 seconds:
Const AFS_PO_MAXTIMETOREACHQUEUE = 20
- For ReceivePO.asp, add the following line before the
call Main() line: Server.ScriptTimeout = 360
- To reduce the transformation time that BizTalk Server takes to
convert a Commerce Server 2002 catalog to the cXML1_1, cXML1_2, or
xCBL3_0 format, you should disable the options for logging interchanges
and original messages.
To disable the logging options
- Open BizTalk Server Administration, expand Microsoft
BizTalk Server 2002, right-click BizTalk Server Group, and
then select Properties.
- In the Properties dialog box, on the Tracking tab,
clear the Log incoming interchange, Log outgoing
interchange, and Log the original MIME encoded message
options. Leave Enable document tracking selected.
- If you publish a catalog using HTTP while the ISA Servers are
disabled, the Business Desk server will report that catalog publishing
was successful because the catalog exists in the AFSCatalogPub shared
folder, when in fact, the catalog does not get published to the site.
- For medium deployments, the Web servers and the Business Desk server
must have unique computer names. Even across separate domains, you might
encounter problems when refreshing catalogs if the computer names are
not unique.
Message Queuing Known Issues
The issues in this section apply to Message Queuing (also known as
MSMQ).
The following steps describe the purchase order acknowledgment process,
and discuss the issues related to this implementation.
- Commerce Server receives the purchase order (through receivepo.asp)
from an external trading partner.
- After initial validation, this XML document is sent to a
protocol-specific remote queue on the BizTalk Server. For example, if a
purchase order using the cXML 1.1 standard is received, it is written to
the cXML1_1PO queue on the BizTalk Server.
- This write operation is transacted with the Message Queuing-specific
transaction command MQ_SINGLE_MESSAGE.
- While writing a message to a remote queue, Message Queuing offers
the following optional parameters for maintaining transactions:
Transaction
Optional. An MSMQTransaction object or one of the following
constants:
MQ_NO_TRANSACTION
Specifies that the call is not part of a transaction.
MQ_MTS_TRANSACTION
Default. Specifies that the call is part of the current MTS
(Microsoft Transaction Server) transaction.
MQ_SINGLE_MESSAGE
Sends a single message as a transaction.
MQ_XA_TRANSACTION
Specifies that the call is part of an externally coordinated,
XA-compliant transaction.
Single-Message Transactions
Message Queuing provides a single-message transaction that can be
used to guarantee a single delivery of a single message. This
transaction implicitly uses the Message Queuing internal transaction to
send a single message to a transactional queue.
Single-message transactions can be used only to send messages.
Note If a
single-message transaction is used to retrieve a message, Message
Queuing disregards the transaction request and retrieves the message
by using a non-transactional operation.
A single-message transaction is a special case of a Message Queuing
internal transaction and cannot participate in a transaction with other
resource managers. Each single-message transaction is a separate
transaction over which the programmer has no explicit commit or abort
control.
The single-message transaction provides the best performance of all
transaction types. In addition to single delivery, a single-message
transaction is faster than an external transaction, and the code used to
send the message is very simple. The sending application only needs to
make sure that the destination queue is transactional and that the
transaction parameter is set to MQ_SINGLE_MESSAGE.
MQ_SINGLE_MESSAGE also means that the transaction is maintained
between the ASP page and the local outgoing queue. After the message is
written to a local outgoing queue, subsequent processing is handled by
the MSMQ Queue Manager.
- The Queue Manager is responsible for sending the message from the
local outgoing queue to the remote, protocol-specific queue.
Transferring the message from the local outgoing queue to the remote
queue is an automatic process controlled by the Queue Manager. The ASP
page does not have any control over this process.
- After the message is written to the remote queue, an acknowledgment
is sent back to an admin queue on the local computer. If the previous
step was successful, the Queue Manager writes an acknowledgment in the
admin queue. The ASP page on the local computer waits for this
acknowledgment on the admin queue.
- After the acknowledgment is received, the ASP page sends an HTTP OK
message back to the trading partner to confirm that the message has been
received successfully by the AFS system.
This process ensures that the purchase order has been successfully
stored on the BizTalk Server before sending acknowledgment back to the
Trading Partner.
- If the admin queue does not receive the confirmation from the remote
queue, the ASP page sends a negative acknowledgment back to the Trading
Partner. It is possible, however, that the purchase order could be
received by the remote queue, and even processed by the system, after
this negative acknowledgment is sent to the trading partner. If this
happens, the trading partner could resend the purchase order, resulting
in duplicate purchase orders.
- If the admin queue on the local computer is not used and an
acknowledgement is sent back to the trading partner as soon as the
message is written to the local outgoing queue, then if the local Queue
Manager is unable to find the remote queue in the given time frame, it
sends the message to the local dead queue. This method requires a
mechanism to monitor the dead queue and notify the system administrator
that an order has failed. If the local computer fails in the meantime,
there is a chance that the system might lose the order. In this case,
acknowledgment has been already sent back to the customer confirming
that the system has received the order.
- The AFS system is designed to prevent purchase orders from being
lost. By using the admin queue, the system ensures that the BizTalk
Server receives the order before sending a confirmation to the Trading
Partner.
URL Resources
The following links provide additional information about the
corresponding subject areas:











